 This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
5. Network Paragraph 3
New transaction broadcasts do not necessarily need to reach all nodes. As long as they reach many nodes, they will get into a block before long. Block broadcasts are also tolerant of dropped messages. If a node does not receive a block, it will request it when it receives the next block and realizes it missed one.
Plain Language
Imagine the Bitcoin game as a giant puzzle game where players are exchanging puzzle pieces. When someone creates a new puzzle piece (transaction), they don't have to show it to everyone, just to a bunch of players. Similarly, when they complete a bigger puzzle (block), even if some players miss it, they can catch up by asking for the details when the next puzzle is solved.
Summary of Section 5: Network
Like a puzzle game, when players (nodes) create a new move (transaction), they don't have to tell every player; like whispering the move to a few friends. When a player finishes solving a puzzle (block) and shares it, other players only accept it if the moves inside are fair, follow the rules and are unused. If some players miss a move, it's OK – they catch up when the next puzzle is solved, making sure the game stays fair and everyone is on the same page.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
5. Network Paragraph 3
New transaction broadcasts do not necessarily need to reach all nodes. As long as they reach many nodes, they will get into a block before long. Block broadcasts are also tolerant of dropped messages. If a node does not receive a block, it will request it when it receives the next block and realizes it missed one.
Plain Language
Imagine the Bitcoin game as a giant puzzle game where players are exchanging puzzle pieces. When someone creates a new puzzle piece (transaction), they don't have to show it to everyone, just to a bunch of players. Similarly, when they complete a bigger puzzle (block), even if some players miss it, they can catch up by asking for the details when the next puzzle is solved.
Summary of Section 5: Network
Like a puzzle game, when players (nodes) create a new move (transaction), they don't have to tell every player; like whispering the move to a few friends. When a player finishes solving a puzzle (block) and shares it, other players only accept it if the moves inside are fair, follow the rules and are unused. If some players miss a move, it's OK – they catch up when the next puzzle is solved, making sure the game stays fair and everyone is on the same page.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
Delta Charlie
npub1aqxs...mhkh
Privacy Protector - Financial Philosopher
Notes (14)
 This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
5. Network Paragraph 3
New transaction broadcasts do not necessarily need to reach all nodes. As long as they reach many nodes, they will get into a block before long. Block broadcasts are also tolerant of dropped messages. If a node does not receive a block, it will request it when it receives the next block and realizes it missed one.
Plain Language
Imagine the Bitcoin game as a giant puzzle game where players are exchanging puzzle pieces. When someone creates a new puzzle piece (transaction), they don't have to show it to everyone, just to a bunch of players. Similarly, when they complete a bigger puzzle (block), even if some players miss it, they can catch up by asking for the details when the next puzzle is solved.
Summary of Section 5: Network
Like a puzzle game, when players (nodes) create a new move (transaction), they don't have to tell every player; like whispering the move to a few friends. When a player finishes solving a puzzle (block) and shares it, other players only accept it if the moves inside are fair, follow the rules and are unused. If some players miss a move, it's OK – they catch up when the next puzzle is solved, making sure the game stays fair and everyone is on the same page.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
5. Network Paragraph 3
New transaction broadcasts do not necessarily need to reach all nodes. As long as they reach many nodes, they will get into a block before long. Block broadcasts are also tolerant of dropped messages. If a node does not receive a block, it will request it when it receives the next block and realizes it missed one.
Plain Language
Imagine the Bitcoin game as a giant puzzle game where players are exchanging puzzle pieces. When someone creates a new puzzle piece (transaction), they don't have to show it to everyone, just to a bunch of players. Similarly, when they complete a bigger puzzle (block), even if some players miss it, they can catch up by asking for the details when the next puzzle is solved.
Summary of Section 5: Network
Like a puzzle game, when players (nodes) create a new move (transaction), they don't have to tell every player; like whispering the move to a few friends. When a player finishes solving a puzzle (block) and shares it, other players only accept it if the moves inside are fair, follow the rules and are unused. If some players miss a move, it's OK – they catch up when the next puzzle is solved, making sure the game stays fair and everyone is on the same page.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
Soft Fork - Like changing some of the game rules so that everyone can keep playing together, and if most players agree to these new rules, they smoothly switch to them without causing a big problem.
5. Network Paragraph 2
Nodes always consider the longest chain to be the correct one and will keep working on extending it. If two nodes broadcast different versions of the next block simultaneously, some nodes may receive one or the other first. In that case, they work on the first one they received, but save the other branch in case it becomes longer. The tie will be broken when the next proof-of-work is found and one branch becomes longer; the nodes that were working on the other branch will then switch to the longer one.
Plain Language
Nodes in Bitcoin are like players in a game. Think of Bitcoin as a game where players (nodes) are constantly trying to solve puzzles to move forward. When they have different ideas about the next move (block), it's like two players suggesting different solutions to the same puzzle at the same time.
Some players might start working on one solution, but they also keep the other one in mind, just like working on multiple puzzle paths. The winner is the first to solve the puzzle, and everyone switches to that solution, breaking any ties to the others and making sure the game moves forward smoothly.
This can also be called a soft fork.
It resembles a situation where there could be a fork in the blockchain. This can happen due to disagreements in the network about which block to consider as the next valid one.
A soft fork is a specific type of change to the Bitcoin system where new rules are introduced, but it remains backward-compatible with the old rules. In the game analogy, a soft fork is like changing some rules of the puzzle-solving game, but players who are still following the old rules can continue playing without any major disruption.
If the majority of players (nodes) accept the new rules or the longer chain following the new rules, it becomes the accepted direction for the game. The nodes that were following the old rules might eventually switch to the new rules if the new chain becomes longer. This transition happens smoothly without creating a permanent split in the chain, which is why it's called a "soft" fork.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
Soft Fork - Like changing some of the game rules so that everyone can keep playing together, and if most players agree to these new rules, they smoothly switch to them without causing a big problem.
5. Network Paragraph 2
Nodes always consider the longest chain to be the correct one and will keep working on extending it. If two nodes broadcast different versions of the next block simultaneously, some nodes may receive one or the other first. In that case, they work on the first one they received, but save the other branch in case it becomes longer. The tie will be broken when the next proof-of-work is found and one branch becomes longer; the nodes that were working on the other branch will then switch to the longer one.
Plain Language
Nodes in Bitcoin are like players in a game. Think of Bitcoin as a game where players (nodes) are constantly trying to solve puzzles to move forward. When they have different ideas about the next move (block), it's like two players suggesting different solutions to the same puzzle at the same time.
Some players might start working on one solution, but they also keep the other one in mind, just like working on multiple puzzle paths. The winner is the first to solve the puzzle, and everyone switches to that solution, breaking any ties to the others and making sure the game moves forward smoothly.
This can also be called a soft fork.
It resembles a situation where there could be a fork in the blockchain. This can happen due to disagreements in the network about which block to consider as the next valid one.
A soft fork is a specific type of change to the Bitcoin system where new rules are introduced, but it remains backward-compatible with the old rules. In the game analogy, a soft fork is like changing some rules of the puzzle-solving game, but players who are still following the old rules can continue playing without any major disruption.
If the majority of players (nodes) accept the new rules or the longer chain following the new rules, it becomes the accepted direction for the game. The nodes that were following the old rules might eventually switch to the new rules if the new chain becomes longer. This transition happens smoothly without creating a permanent split in the chain, which is why it's called a "soft" fork.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
5. Network Paragraph 1
The steps to run the network are as follows:
1) New transactions are broadcast to all nodes.
2) Each node collects new transactions into a block.
3) Each node works on finding a difficult proof-of-work for its block.
4) When a node finds a proof-of-work, it broadcasts the block to all nodes.
5) Nodes accept the block only if all transactions in it are valid and not already spent.
6) Nodes express their acceptance of the block by working on creating the next block in the chain, using the hash of the accepted block as the previous hash.
Plain Language
The steps to run the network are as follows:
1) The network is like a digital bulletin board where people post their transactions. Everyone in the network knows what's happening.
2) All those transactions get grouped together into a block. Like a batch of transactions or processes people want to have verified.
3) The challenge: solving a complex puzzle (proof-of-work) for the block. Once solved, the first one to solve it gets to announce their success to the whole network.
4) The winner broadcasts their block to everyone like a scoreboard to the puzzle game.
5) However, the other participants only accept the block if all the transactions in it are legit and haven't been used before.
6) Now, since they've successfully added a block, computers gear up for the next challenge. They create a new block, linking it to the previous one. Like a continuous chain of puzzles, ensuring a secure and organized environment for transactions.
Said another way, being a node is like being a referee, checking every move to keep the game fair. If a node accepts a block, it's not just sitting there – it's already thinking about the next round, linking it to the previous one and keeping the game going.
In a nutshell, the Bitcoin network is like a digital challenge playground and competition where participants work together to validate and secure transactions through solving complex puzzles.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
5. Network Paragraph 1
The steps to run the network are as follows:
1) New transactions are broadcast to all nodes.
2) Each node collects new transactions into a block.
3) Each node works on finding a difficult proof-of-work for its block.
4) When a node finds a proof-of-work, it broadcasts the block to all nodes.
5) Nodes accept the block only if all transactions in it are valid and not already spent.
6) Nodes express their acceptance of the block by working on creating the next block in the chain, using the hash of the accepted block as the previous hash.
Plain Language
The steps to run the network are as follows:
1) The network is like a digital bulletin board where people post their transactions. Everyone in the network knows what's happening.
2) All those transactions get grouped together into a block. Like a batch of transactions or processes people want to have verified.
3) The challenge: solving a complex puzzle (proof-of-work) for the block. Once solved, the first one to solve it gets to announce their success to the whole network.
4) The winner broadcasts their block to everyone like a scoreboard to the puzzle game.
5) However, the other participants only accept the block if all the transactions in it are legit and haven't been used before.
6) Now, since they've successfully added a block, computers gear up for the next challenge. They create a new block, linking it to the previous one. Like a continuous chain of puzzles, ensuring a secure and organized environment for transactions.
Said another way, being a node is like being a referee, checking every move to keep the game fair. If a node accepts a block, it's not just sitting there – it's already thinking about the next round, linking it to the previous one and keeping the game going.
In a nutshell, the Bitcoin network is like a digital challenge playground and competition where participants work together to validate and secure transactions through solving complex puzzles.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
4. Proof-of-Work Paragraph 4
To compensate for increasing hardware speed and varying interest in running nodes over time, the proof-of-work difficulty is determined by a moving average targeting an average number of blocks per hour. If they’re generated too fast, the difficulty increases.
Plain Language
Say we're playing a game, and we want to make sure it's not too easy or too hard. The game adjusts itself based on how quickly or slowly we're playing, roughly every two weeks.
With computers, and the game we're playing, we call this adjustment "proof-of-work difficulty." We're changing the difficulty to keep things fair. We want a certain number of new game levels (blocks) to be created every hour. If we're finishing levels too quickly, the game makes it a bit tougher to slow us down and keep the rules fair. The network is set to create new blocks roughly every 10 minutes.
So, the proof-of-work difficulty is like having a game that adapts to how fast or slow we're going, making sure the rules stay the same for everyone playing.
Currently, the bitcoin network adjusts its proof-of-work difficulty every 2016 blocks, which roughly translates to about two weeks. This adjustment is designed to ensure that the average time it takes to produce a block stays close to 10 minutes.
In summary:
- Previous Blocks: The network looks at the last 2016 blocks created
- Time Calculation: It calculates how long it took to mine those 2016 blocks
- Adjustment: If it took less than two weeks, blocks were mined too quickly, difficulty increases. If it took more than two weeks, blocks were mined too slowly, difficulty decreases.
This process occurs approximately every two weeks to maintain a consistent block generation time of around 10 minutes. A powerful self-regulating system requiring no outside parties.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
4. Proof-of-Work Paragraph 4
To compensate for increasing hardware speed and varying interest in running nodes over time, the proof-of-work difficulty is determined by a moving average targeting an average number of blocks per hour. If they’re generated too fast, the difficulty increases.
Plain Language
Say we're playing a game, and we want to make sure it's not too easy or too hard. The game adjusts itself based on how quickly or slowly we're playing, roughly every two weeks.
With computers, and the game we're playing, we call this adjustment "proof-of-work difficulty." We're changing the difficulty to keep things fair. We want a certain number of new game levels (blocks) to be created every hour. If we're finishing levels too quickly, the game makes it a bit tougher to slow us down and keep the rules fair. The network is set to create new blocks roughly every 10 minutes.
So, the proof-of-work difficulty is like having a game that adapts to how fast or slow we're going, making sure the rules stay the same for everyone playing.
Currently, the bitcoin network adjusts its proof-of-work difficulty every 2016 blocks, which roughly translates to about two weeks. This adjustment is designed to ensure that the average time it takes to produce a block stays close to 10 minutes.
In summary:
- Previous Blocks: The network looks at the last 2016 blocks created
- Time Calculation: It calculates how long it took to mine those 2016 blocks
- Adjustment: If it took less than two weeks, blocks were mined too quickly, difficulty increases. If it took more than two weeks, blocks were mined too slowly, difficulty decreases.
This process occurs approximately every two weeks to maintain a consistent block generation time of around 10 minutes. A powerful self-regulating system requiring no outside parties.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
IP address - Internet Protocol, a number that reveals the location of a computer or device
4. Proof-of-Work Paragraph 3
The proof-of-work also solves the problem of determining representation in majority decision making. If the majority were based on one-IP-address-one-vote, it could be subverted by anyone able to allocate many IPs. Proof-of-work is essentially one-CPU-one-vote. The majority decision is represented by the longest chain, which has the greatest proof-of-work effort invested in it. If a majority of CPU power is controlled by honest nodes, the honest chain will grow the fastest and outpace any competing chains. To modify a past block, an attacker would have to redo the proof-of-work of the block and all blocks after it and then catch up with and surpass the work of the honest nodes. We will show later that the probability of a slower attacker catching up diminishes exponentially as subsequent blocks are added.
Plain Language
Imagine we're all in a big group, and we need to decide something together. Instead of each person having one vote, we use a special way called proof-of-work to vote. Each person's vote is based on how much work the computer can do. The vote is not based on the IP address (location) of the computer. IP addresses can be easily manipulated.
For example, if someone has 20 computers in one building, with one Internet connection, they have one IP address. If someone has one computer, at a location with an Internet connection, they also have one IP address. With this system, the 2 people are equal, and that is not what proof-of-work is about. The person with more computing power is contributing more to the network, so they get 20 votes. The person with one computer is contributing less to the network, so they get a single vote.
If someone tries to cheat by pretending to be many people with different computer addresses, proof-of-work helps stop them. It's like saying, "one computer, one vote." The decision we all agree on is the one that comes with the longest chain of proven work.
Imagine building a tower made of building blocks, and each block represents the work done by a computer. If most of the computers are doing their job honestly, our tower (or chain) grows the fastest. If someone wants to change something we did in the past, they have to redo all the work done by all the computers and build an even taller tower. Very difficult to catch up and beat the honest computers.
So, proof-of-work makes sure that if most of the computers are being honest, our decisions are safe and hard to change. The more blocks we add to our tower, the less likely it is that someone trying to cheat can catch up with us.
The block height at the time of this writing is 825,310 and the blockchain is about 540GB in size.
Check block height here:
https://live.blockcypher.com/btc/block/00000000000000000003d61a48a55bcc1d7aaa2ccb5eb9268f1458bbecc6c9d7/
Check blockchain size here:
https://ycharts.com/indicators/bitcoin_blockchain_size
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
IP address - Internet Protocol, a number that reveals the location of a computer or device
4. Proof-of-Work Paragraph 3
The proof-of-work also solves the problem of determining representation in majority decision making. If the majority were based on one-IP-address-one-vote, it could be subverted by anyone able to allocate many IPs. Proof-of-work is essentially one-CPU-one-vote. The majority decision is represented by the longest chain, which has the greatest proof-of-work effort invested in it. If a majority of CPU power is controlled by honest nodes, the honest chain will grow the fastest and outpace any competing chains. To modify a past block, an attacker would have to redo the proof-of-work of the block and all blocks after it and then catch up with and surpass the work of the honest nodes. We will show later that the probability of a slower attacker catching up diminishes exponentially as subsequent blocks are added.
Plain Language
Imagine we're all in a big group, and we need to decide something together. Instead of each person having one vote, we use a special way called proof-of-work to vote. Each person's vote is based on how much work the computer can do. The vote is not based on the IP address (location) of the computer. IP addresses can be easily manipulated.
For example, if someone has 20 computers in one building, with one Internet connection, they have one IP address. If someone has one computer, at a location with an Internet connection, they also have one IP address. With this system, the 2 people are equal, and that is not what proof-of-work is about. The person with more computing power is contributing more to the network, so they get 20 votes. The person with one computer is contributing less to the network, so they get a single vote.
If someone tries to cheat by pretending to be many people with different computer addresses, proof-of-work helps stop them. It's like saying, "one computer, one vote." The decision we all agree on is the one that comes with the longest chain of proven work.
Imagine building a tower made of building blocks, and each block represents the work done by a computer. If most of the computers are doing their job honestly, our tower (or chain) grows the fastest. If someone wants to change something we did in the past, they have to redo all the work done by all the computers and build an even taller tower. Very difficult to catch up and beat the honest computers.
So, proof-of-work makes sure that if most of the computers are being honest, our decisions are safe and hard to change. The more blocks we add to our tower, the less likely it is that someone trying to cheat can catch up with us.
The block height at the time of this writing is 825,310 and the blockchain is about 540GB in size.
Check block height here:
https://live.blockcypher.com/btc/block/00000000000000000003d61a48a55bcc1d7aaa2ccb5eb9268f1458bbecc6c9d7/
Check blockchain size here:
https://ycharts.com/indicators/bitcoin_blockchain_size
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr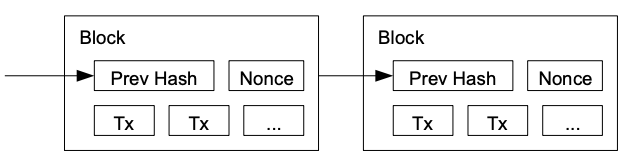 This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Tx - transaction
nonce - number only used once
4. Proof-of-Work Paragraph 2
For our timestamp network, we implement the proof-of-work by incrementing a nonce in the block until a value is found that gives the block’s hash the required zero bits. Once the CPU effort has been expended to make it satisfy the proof-of-work, the block cannot be changed without redoing the work. As later blocks are chained after it, the work to change the block would include redoing all the blocks after it.
Plain Language
Imagine you have a lockbox, protected by a special lock. This lock is a challenge – it only opens if you can find the secret number. The catch is: the secret number has to have a specific number of zeros at the beginning.
The chances of guessing the right number are currently 1 in 4,294,967,296.
To find this secret number, you start with another number called a "nonce" and keep trying different ones(nonce numbers) until you discover the secret number that makes the lock open with the correct number of zeros at the beginning of the number. Once you find it, you lock the lockbox with this specific number.
Find the secret number, lock the lockbox using that number.
The next part: once the computer has gone through all the effort to find the right number, it locks the lockbox, making it very difficult for anyone to change it. If someone wants to attack the lockbox, they would have to redo all the work you did, finding the secret number.
If your lockbox is part of a group of lockboxes, chained together(blockchain), changing one would mean redoing all the work for every lockbox in the chain. This gives the network, and the information very high security.
There is currently no ability, or incentive, to try to attack this system. To break this system, a tremendous amount of resources would have to attack every single device on the planet that has a copy of this information.
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Tx - transaction
nonce - number only used once
4. Proof-of-Work Paragraph 2
For our timestamp network, we implement the proof-of-work by incrementing a nonce in the block until a value is found that gives the block’s hash the required zero bits. Once the CPU effort has been expended to make it satisfy the proof-of-work, the block cannot be changed without redoing the work. As later blocks are chained after it, the work to change the block would include redoing all the blocks after it.
Plain Language
Imagine you have a lockbox, protected by a special lock. This lock is a challenge – it only opens if you can find the secret number. The catch is: the secret number has to have a specific number of zeros at the beginning.
The chances of guessing the right number are currently 1 in 4,294,967,296.
To find this secret number, you start with another number called a "nonce" and keep trying different ones(nonce numbers) until you discover the secret number that makes the lock open with the correct number of zeros at the beginning of the number. Once you find it, you lock the lockbox with this specific number.
Find the secret number, lock the lockbox using that number.
The next part: once the computer has gone through all the effort to find the right number, it locks the lockbox, making it very difficult for anyone to change it. If someone wants to attack the lockbox, they would have to redo all the work you did, finding the secret number.
If your lockbox is part of a group of lockboxes, chained together(blockchain), changing one would mean redoing all the work for every lockbox in the chain. This gives the network, and the information very high security.
There is currently no ability, or incentive, to try to attack this system. To break this system, a tremendous amount of resources would have to attack every single device on the planet that has a copy of this information.
 #bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr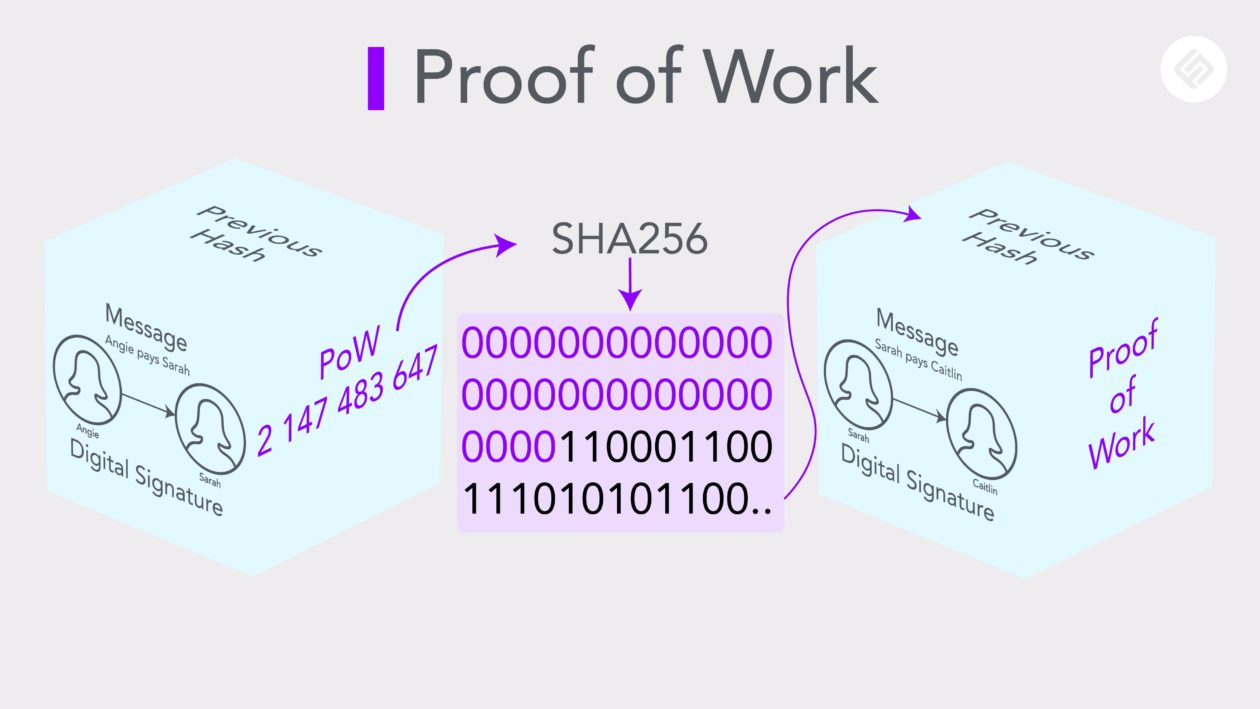 This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
4. Proof-of-Work Paragraph 1
To implement a distributed timestamp server on a peer-to-peer basis, we will need to use a proof-of-work system similar to Adam Back’s Hashcash[6], rather than newspaper or Usenet posts. The proof-of-work involves scanning for a value that when hashed, such as with SHA-256(encryption tools that scramble information), the hash begins with a number of zero bits. The average work required is exponential in the number of zero bits required and can be verified by executing a single hash.
Plain Language
To create a timestamp server that works in a shared network without a central authority, we'll use a proof-of-work system like Adam Back's Hashcash, instead of relying on newspapers or online posts.
The proof-of-work process includes:
- searching for a specific value("guess the number" game)
- when this value is hashed using a method like SHA-256(encryption tools)
- the resulting hash(information)
- must start with a certain number of zeros(the secret number)
Said another way: get random puzzle, computer does work, try to guess the right number before anyone else.
Guess the number, win a prize. The chances of guessing the right number are currently 1 in 4,294,967,296.
Getting the right number of zeros is what makes the process challenging. The more zeros required, the more computing power you need to put in.
So, when someone wants to check if you did the work, they have to take your scrambled information, use the SHA-256 tools, and see if the code starts with the correct number of zeros. If it does, that means you've successfully proven that you did the work.
The computing power needed for this increases with the number of zeros required in the secret number. The "puzzle" is difficult to solve, but once it is solved, the results are easily read and verified by everyone else.
Think Sudoku or Tic-Tac-Toe; challenging to play, easy to see who won the game.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
4. Proof-of-Work Paragraph 1
To implement a distributed timestamp server on a peer-to-peer basis, we will need to use a proof-of-work system similar to Adam Back’s Hashcash[6], rather than newspaper or Usenet posts. The proof-of-work involves scanning for a value that when hashed, such as with SHA-256(encryption tools that scramble information), the hash begins with a number of zero bits. The average work required is exponential in the number of zero bits required and can be verified by executing a single hash.
Plain Language
To create a timestamp server that works in a shared network without a central authority, we'll use a proof-of-work system like Adam Back's Hashcash, instead of relying on newspapers or online posts.
The proof-of-work process includes:
- searching for a specific value("guess the number" game)
- when this value is hashed using a method like SHA-256(encryption tools)
- the resulting hash(information)
- must start with a certain number of zeros(the secret number)
Said another way: get random puzzle, computer does work, try to guess the right number before anyone else.
Guess the number, win a prize. The chances of guessing the right number are currently 1 in 4,294,967,296.
Getting the right number of zeros is what makes the process challenging. The more zeros required, the more computing power you need to put in.
So, when someone wants to check if you did the work, they have to take your scrambled information, use the SHA-256 tools, and see if the code starts with the correct number of zeros. If it does, that means you've successfully proven that you did the work.
The computing power needed for this increases with the number of zeros required in the secret number. The "puzzle" is difficult to solve, but once it is solved, the results are easily read and verified by everyone else.
Think Sudoku or Tic-Tac-Toe; challenging to play, easy to see who won the game.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr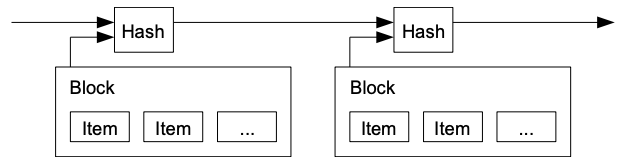 This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
3. Timestamp Server
The solution we propose begins with a timestamp server. A timestamp server works by taking a hash of a block of items to be timestamped and widely publishing the hash, such as in a newspaper or Usenet post[2-5]. The timestamp proves that the data must have existed at the time, obviously, in order to get into the hash. Each timestamp includes the previous timestamp in its hash, forming a chain, with each additional timestamp reinforcing the ones before it.
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
3. Timestamp Server
The solution we propose begins with a timestamp server. A timestamp server works by taking a hash of a block of items to be timestamped and widely publishing the hash, such as in a newspaper or Usenet post[2-5]. The timestamp proves that the data must have existed at the time, obviously, in order to get into the hash. Each timestamp includes the previous timestamp in its hash, forming a chain, with each additional timestamp reinforcing the ones before it.
 Plain Language
Imagine you want to prove that you had a certain piece of information at a specific time. We can use something called a timestamp server. This server takes a unique code (hash) of the information and shares it publicly, like in a newspaper or online post.
This code, or timestamp, acts as proof that the information existed at that time because it's tied to the hash. Each new timestamp also includes the previous one, creating a chain(blockchain). If you ever need to show when you had certain data, you can use this chain of timestamps as evidence.
Plain Language
Imagine you want to prove that you had a certain piece of information at a specific time. We can use something called a timestamp server. This server takes a unique code (hash) of the information and shares it publicly, like in a newspaper or online post.
This code, or timestamp, acts as proof that the information existed at that time because it's tied to the hash. Each new timestamp also includes the previous one, creating a chain(blockchain). If you ever need to show when you had certain data, you can use this chain of timestamps as evidence.
 #bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
2. Transactions Paragraph 3
We need a way for the payee to know that the previous owners did not sign any earlier transactions. For our purposes, the earliest transaction is the one that counts, so we don’t care about later attempts to double-spend. The only way to confirm the absence of a transaction is to be aware of all transactions. In the mint based model, the mint was aware of all transactions and decided which arrived first. To accomplish this without a trusted party, transactions must be publicly announced[1], and we need a system for participants to agree on a single history of the order in which they were received. The payee needs proof that at the time of each transaction, the majority of nodes agreed it was the first received.
Plain Language
We want to make sure that the person receiving the digital coin knows that the people who had it before didn't use it in any previous transactions. However, for us, only the very first transaction matters, and we're not concerned about any attempts to spend the coin again later.
To confirm that a transaction didn't happen before, we need to know about all the transactions. In the previous system with the central authority, they knew about every transaction and decided which one happened first. Now, without relying on a trusted authority, we need transactions to be publicly announced. Additionally, we need a way for everyone involved to agree on the order in which these transactions occurred.
The person receiving the coin needs evidence that, at the time of each transaction, most of the participants in the network agreed it was the first one to be received. This way, we can be confident about the order of transactions and make sure the digital coin is used properly.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
2. Transactions Paragraph 3
We need a way for the payee to know that the previous owners did not sign any earlier transactions. For our purposes, the earliest transaction is the one that counts, so we don’t care about later attempts to double-spend. The only way to confirm the absence of a transaction is to be aware of all transactions. In the mint based model, the mint was aware of all transactions and decided which arrived first. To accomplish this without a trusted party, transactions must be publicly announced[1], and we need a system for participants to agree on a single history of the order in which they were received. The payee needs proof that at the time of each transaction, the majority of nodes agreed it was the first received.
Plain Language
We want to make sure that the person receiving the digital coin knows that the people who had it before didn't use it in any previous transactions. However, for us, only the very first transaction matters, and we're not concerned about any attempts to spend the coin again later.
To confirm that a transaction didn't happen before, we need to know about all the transactions. In the previous system with the central authority, they knew about every transaction and decided which one happened first. Now, without relying on a trusted authority, we need transactions to be publicly announced. Additionally, we need a way for everyone involved to agree on the order in which these transactions occurred.
The person receiving the coin needs evidence that, at the time of each transaction, most of the participants in the network agreed it was the first one to be received. This way, we can be confident about the order of transactions and make sure the digital coin is used properly.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr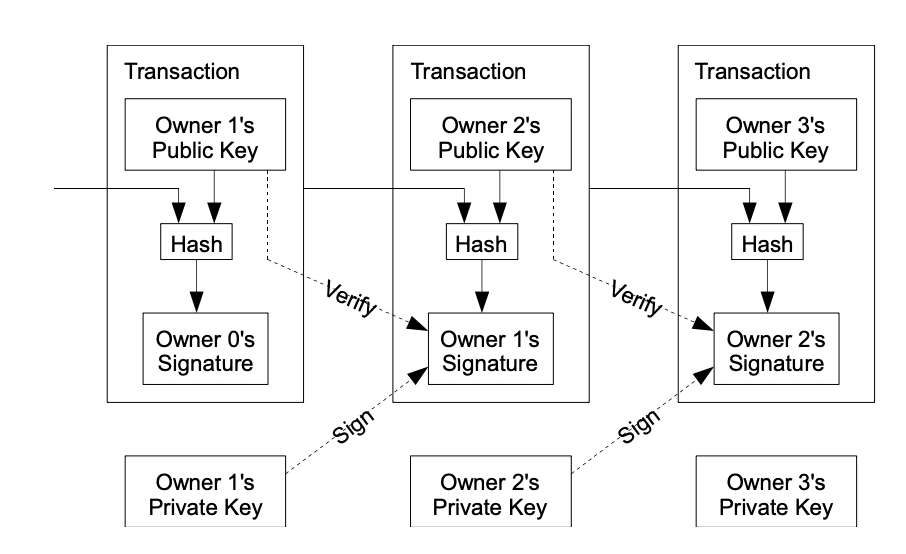 Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
2. Transactions Paragraph 1 and 2
We define an electronic coin as a chain of digital signatures. Each owner transfers the coin to the next by digitally signing a hash of the previous transaction and the public key of the next owner and adding these to the end of the coin. A payee can verify the signatures to verify the chain of ownership.
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
2. Transactions Paragraph 1 and 2
We define an electronic coin as a chain of digital signatures. Each owner transfers the coin to the next by digitally signing a hash of the previous transaction and the public key of the next owner and adding these to the end of the coin. A payee can verify the signatures to verify the chain of ownership.
 The problem of course is the payee can’t verify that one of the owners did not double-spend the coin. A common solution is to introduce a trusted central authority, or mint, that checks every transaction for double spending. After each transaction, the coin must be returned to the mint to issue a new coin, and only coins issued directly from the mint are trusted not to be double-spent. The problem with this solution is that the fate of the entire money system depends on the company running the mint, with every transaction having to go through them, just like a bank.
Plain Language
These electronic coins act a like digital chain of information. When you own this digital coin and want to give it to someone else, you "sign" it digitally. This involves creating a unique code that includes information about the previous transaction and the new owner's public key. This code is then added to the end of the digital coin.
Now, if someone receives the coin, they can check these digital signatures to make sure the chain of ownership is legitimate. Like a way of making sure that the history of the coin and who owns it is secure and reliable.
The problem of course is the payee can’t verify that one of the owners did not double-spend the coin. A common solution is to introduce a trusted central authority, or mint, that checks every transaction for double spending. After each transaction, the coin must be returned to the mint to issue a new coin, and only coins issued directly from the mint are trusted not to be double-spent. The problem with this solution is that the fate of the entire money system depends on the company running the mint, with every transaction having to go through them, just like a bank.
Plain Language
These electronic coins act a like digital chain of information. When you own this digital coin and want to give it to someone else, you "sign" it digitally. This involves creating a unique code that includes information about the previous transaction and the new owner's public key. This code is then added to the end of the digital coin.
Now, if someone receives the coin, they can check these digital signatures to make sure the chain of ownership is legitimate. Like a way of making sure that the history of the coin and who owns it is secure and reliable.
 The issue here is that the person receiving the digital coin can't be sure that the person who gave it to them didn't try to spend the same coin again somewhere else. To solve this problem, some suggest having a trusted central authority, like a bank, that checks every transaction to make sure no one is trying to spend the same coin twice.
The catch, though, is after each transaction, the coin has to go back to this central authority, and they issue a new coin. The idea is that only coins directly issued by this authority can be trusted not to be double-spent.
The problem is that the entire money system relies on this central authority. Every transaction has to go through them, similar to how transactions go through a bank. This can be a drawback because the whole system depends on the trustworthiness of the company, or people, running this central authority.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
The issue here is that the person receiving the digital coin can't be sure that the person who gave it to them didn't try to spend the same coin again somewhere else. To solve this problem, some suggest having a trusted central authority, like a bank, that checks every transaction to make sure no one is trying to spend the same coin twice.
The catch, though, is after each transaction, the coin has to go back to this central authority, and they issue a new coin. The idea is that only coins directly issued by this authority can be trusted not to be double-spent.
The problem is that the entire money system relies on this central authority. Every transaction has to go through them, similar to how transactions go through a bank. This can be a drawback because the whole system depends on the trustworthiness of the company, or people, running this central authority.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Introduction Paragraph 2
What is needed is an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust, allowing any two willing parties to transact directly with each other without the need for a trusted third party. Transactions that are computationally impractical to reverse would protect sellers from fraud, and routine escrow mechanisms could easily be implemented to protect buyers. In this paper, we propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer distributed timestamp server to generate computational proof of the chronological order of transactions. The system is secure as long as honest nodes collectively control more CPU power than any cooperating group of attacker nodes.
Plain Language
We need a way to pay for things online without relying so much on trust and middlemen like banks. Imagine a system where you and another person can directly make transactions without needing a third party to oversee everything. To prevent fraud, we want transactions that are practically impossible to reverse.
In our idea, we suggest using a peer-to-peer system with a special server to keep track of when transactions happen. This server helps us prove the order of transactions through advanced computer work. As long as the good guys have more computing power than any group of bad guys, our system stays secure. It's a digital way of making sure everything happens in the right order without someone trying to cheat the system.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Introduction Paragraph 2
What is needed is an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust, allowing any two willing parties to transact directly with each other without the need for a trusted third party. Transactions that are computationally impractical to reverse would protect sellers from fraud, and routine escrow mechanisms could easily be implemented to protect buyers. In this paper, we propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer distributed timestamp server to generate computational proof of the chronological order of transactions. The system is secure as long as honest nodes collectively control more CPU power than any cooperating group of attacker nodes.
Plain Language
We need a way to pay for things online without relying so much on trust and middlemen like banks. Imagine a system where you and another person can directly make transactions without needing a third party to oversee everything. To prevent fraud, we want transactions that are practically impossible to reverse.
In our idea, we suggest using a peer-to-peer system with a special server to keep track of when transactions happen. This server helps us prove the order of transactions through advanced computer work. As long as the good guys have more computing power than any group of bad guys, our system stays secure. It's a digital way of making sure everything happens in the right order without someone trying to cheat the system.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Original
1. Introduction Paragraph 1
Commerce on the Internet has come to rely almost exclusively on financial institutions serving as trusted third parties to process electronic payments. While the system works well enough for most transactions, it still suffers from the inherent weaknesses of the trust based model. Completely non-reversible transactions are not really possible, since financial institutions cannot avoid mediating disputes. The cost of mediation increases transaction costs, limiting the minimum practical transaction size and cutting off the possibility for small casual transactions, and there is a broader cost in the loss of ability to make non-reversible payments for non-reversible services. With the possibility of reversal, the need for trust spreads. Merchants must be wary of their customers, hassling them for more information than they would otherwise need. A certain percentage of fraud is accepted as unavoidable. These costs and payment uncertainties can be avoided in person by using physical currency, but no mechanism exists to make payments over a communications channel without a trusted party.
Plain Language
When we buy things online, we usually rely on banks or other trusted companies to "handle" the money. It works fine most of the time, but there are some issues. For example, once we pay, it's not always possible to undo the transaction if there's a problem. Banks have to step in to solve disputes, which adds extra costs and makes small transactions more difficult.
This reliance on trust also means that merchants have to be careful with every customer, asking for more information than they would really need. There's always a risk of fraud, and we just accept that some amount of cheating is unavoidable.
When we use physical money in person, we can avoid these issues, but when it comes to paying over the Internet without involving a trusted middleman, there's currently no good system in place.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Original
1. Introduction Paragraph 1
Commerce on the Internet has come to rely almost exclusively on financial institutions serving as trusted third parties to process electronic payments. While the system works well enough for most transactions, it still suffers from the inherent weaknesses of the trust based model. Completely non-reversible transactions are not really possible, since financial institutions cannot avoid mediating disputes. The cost of mediation increases transaction costs, limiting the minimum practical transaction size and cutting off the possibility for small casual transactions, and there is a broader cost in the loss of ability to make non-reversible payments for non-reversible services. With the possibility of reversal, the need for trust spreads. Merchants must be wary of their customers, hassling them for more information than they would otherwise need. A certain percentage of fraud is accepted as unavoidable. These costs and payment uncertainties can be avoided in person by using physical currency, but no mechanism exists to make payments over a communications channel without a trusted party.
Plain Language
When we buy things online, we usually rely on banks or other trusted companies to "handle" the money. It works fine most of the time, but there are some issues. For example, once we pay, it's not always possible to undo the transaction if there's a problem. Banks have to step in to solve disputes, which adds extra costs and makes small transactions more difficult.
This reliance on trust also means that merchants have to be careful with every customer, asking for more information than they would really need. There's always a risk of fraud, and we just accept that some amount of cheating is unavoidable.
When we use physical money in person, we can avoid these issues, but when it comes to paying over the Internet without involving a trusted middleman, there's currently no good system in place.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
The following series will translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language for the nostr audience. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language following.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Original
Abstract. A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution. Digital signatures provide part of the solution, but the main benefits are lost if a trusted third party is still required to prevent double-spending. We propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer network. The network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing the proof-of-work. The longest chain not only serves as proof of the sequence of events witnessed, but proof that it came from the largest pool of CPU power. As long as a majority of CPU power is controlled by nodes that are not cooperating to attack the network, they’ll generate the longest chain and outpace attackers. The network itself requires minimal structure. Messages are broadcast on a best effort basis, and nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the longest proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone.
Plain Language
Imagine you have a way to trade things online, and you don't need any banks or outsiders to help out. Like a secret code that makes sure no one cheats and spends the same money twice.
Here's the tricky part: sometimes, you still need someone to make sure nobody's manipulating the system. The solution: instead of having just one person in charge, everyone participates in the system. Every time someone trades something, we write it down on a special list and solve a puzzle to make sure it's a real trade.
This list keeps growing. The longest list, with the most puzzles solved, becomes the official record of all the trades. It's so strong that nobody can change it or cheat because it would take too much work to redo all the puzzles.
The people trading are very easygoing. People can come and go as they want, and we still trust the longest list to show us what happened when someone was away. As long as most people in our team are playing fair and not trying to mess things up, our trading system stays safe and works well.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
The following series will translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language for the nostr audience. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language following.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Original
Abstract. A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution. Digital signatures provide part of the solution, but the main benefits are lost if a trusted third party is still required to prevent double-spending. We propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer network. The network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing the proof-of-work. The longest chain not only serves as proof of the sequence of events witnessed, but proof that it came from the largest pool of CPU power. As long as a majority of CPU power is controlled by nodes that are not cooperating to attack the network, they’ll generate the longest chain and outpace attackers. The network itself requires minimal structure. Messages are broadcast on a best effort basis, and nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the longest proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone.
Plain Language
Imagine you have a way to trade things online, and you don't need any banks or outsiders to help out. Like a secret code that makes sure no one cheats and spends the same money twice.
Here's the tricky part: sometimes, you still need someone to make sure nobody's manipulating the system. The solution: instead of having just one person in charge, everyone participates in the system. Every time someone trades something, we write it down on a special list and solve a puzzle to make sure it's a real trade.
This list keeps growing. The longest list, with the most puzzles solved, becomes the official record of all the trades. It's so strong that nobody can change it or cheat because it would take too much work to redo all the puzzles.
The people trading are very easygoing. People can come and go as they want, and we still trust the longest list to show us what happened when someone was away. As long as most people in our team are playing fair and not trying to mess things up, our trading system stays safe and works well.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr Doctrine Puts Citizens, Laws, and Prosperity on the Chopping Block - Sacrifices Made in the Primal Pursuit of Self-Survival
From The Creature from Jekyll Island, 5th Edition, Chapter 11 The Rothschild Formula:
“If such a man were to survey the world around him, it is not difficult to imagine that he would come to the following conclusions which would become the prime directives of his career:
War is the ultimate discipline to any government. If it can
successfully meet the challenge of war, it will survive. If it
cannot, it will perish. All else is secondary. The sanctity of its
laws, the prosperity of its citizens, and the solvency of its
treasury will be quickly sacrificed by any government in its
primal act of self-survival.”
In this worldview, war emerges as the litmus test for governmental resilience. Survival hinges on conquering the challenges of war, making all else—laws, prosperity, and fiscal health—secondary. Governments, driven by primal self-preservation, prioritize the brutality of conflict over the well-being of citizens and the integrity of their institutions.
#gedwardgriffin #jekyllisland #gold #silver #bitcoin #federalreserve #endthefed #government #war #inflation #rothschild #money #war
Doctrine Puts Citizens, Laws, and Prosperity on the Chopping Block - Sacrifices Made in the Primal Pursuit of Self-Survival
From The Creature from Jekyll Island, 5th Edition, Chapter 11 The Rothschild Formula:
“If such a man were to survey the world around him, it is not difficult to imagine that he would come to the following conclusions which would become the prime directives of his career:
War is the ultimate discipline to any government. If it can
successfully meet the challenge of war, it will survive. If it
cannot, it will perish. All else is secondary. The sanctity of its
laws, the prosperity of its citizens, and the solvency of its
treasury will be quickly sacrificed by any government in its
primal act of self-survival.”
In this worldview, war emerges as the litmus test for governmental resilience. Survival hinges on conquering the challenges of war, making all else—laws, prosperity, and fiscal health—secondary. Governments, driven by primal self-preservation, prioritize the brutality of conflict over the well-being of citizens and the integrity of their institutions.
#gedwardgriffin #jekyllisland #gold #silver #bitcoin #federalreserve #endthefed #government #war #inflation #rothschild #money #war