 What content would you like to see?
Writing the whitepaper in plain language was halted right before the last part, which is the more technical part of the paper. I wanted to see if there was overall interest before continuing with this more challenging section.
I also have started another series, that explains money in plain language. I draw from the traditional rules of money:
-medium of exchange
-unit of account
-portable
-durable
-divisible
-fungible (interchangeable)
-store of value
Should we continue with the whitepaper? Or would you like to see the money paper?
What content would you like to see?
Writing the whitepaper in plain language was halted right before the last part, which is the more technical part of the paper. I wanted to see if there was overall interest before continuing with this more challenging section.
I also have started another series, that explains money in plain language. I draw from the traditional rules of money:
-medium of exchange
-unit of account
-portable
-durable
-divisible
-fungible (interchangeable)
-store of value
Should we continue with the whitepaper? Or would you like to see the money paper?

Delta Charlie
npub1aqxs...mhkh
Privacy Protector - Financial Philosopher
Notes (13)
 What content would you like to see?
Writing the whitepaper in plain language was halted right before the last part, which is the more technical part of the paper. I wanted to see if there was overall interest before continuing with this more challenging section.
I also have started another series, that explains money in plain language. I draw from the traditional rules of money:
-medium of exchange
-unit of account
-portable
-durable
-divisible
-fungible (interchangeable)
-store of value
Should we continue with the whitepaper? Or would you like to see the money paper?
What content would you like to see?
Writing the whitepaper in plain language was halted right before the last part, which is the more technical part of the paper. I wanted to see if there was overall interest before continuing with this more challenging section.
I also have started another series, that explains money in plain language. I draw from the traditional rules of money:
-medium of exchange
-unit of account
-portable
-durable
-divisible
-fungible (interchangeable)
-store of value
Should we continue with the whitepaper? Or would you like to see the money paper?
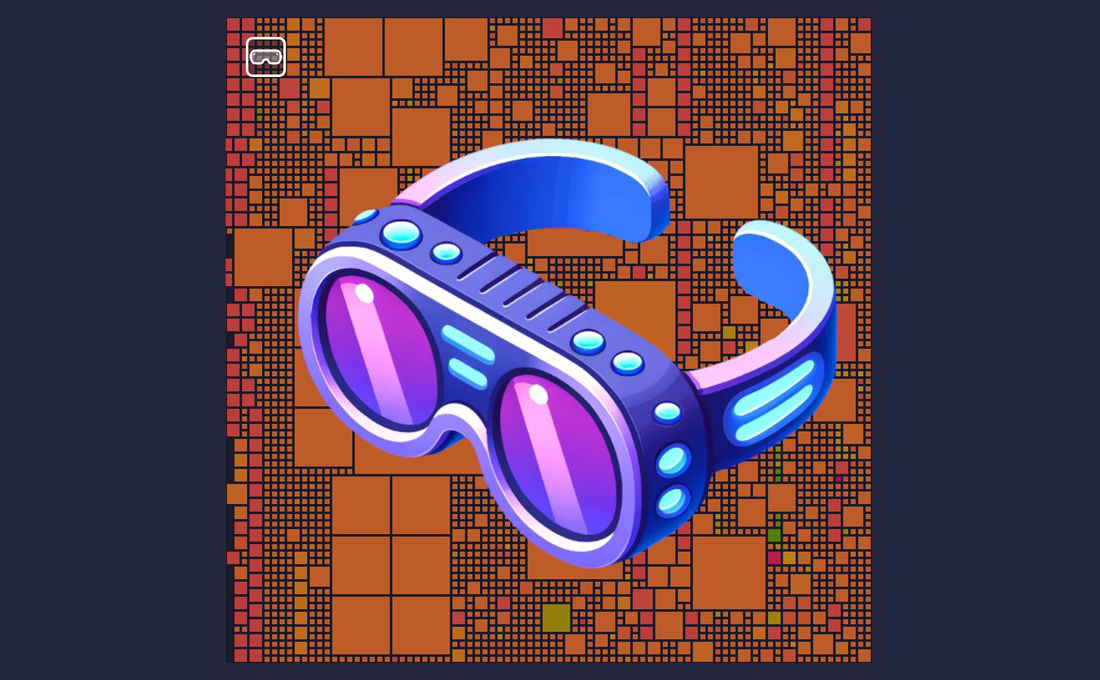 Recently learned about a fairly new feature in the mempool: Mempool Goggles.
This lets the user target certain blocks, and activity within those blocks, such as a coinjoin.
As freedom tech evolves, the cat and mouse game continues.
This article explores Mempool Goggles: https://www.nobsbitcoin.com/introducing-mempool-goggles/
This article explores bitcoin fungibility in an increasingly surveilled environment: https://sethforprivacy.com/posts/fungibility-graveyard/
Thanks to the following for an enlightening and civilized discussion: nostr:npub1ppjkfvk0ek3g584gp7qp9d3znwdznadchet7q2aez9r27620n9zs45xvx2 nostr:npub14a6q6xvt4wuv0wpdpfr336e4fweldtu6np3ehpw55h83xuw2h2zsgyz6rn nostr:npub1tr4dstaptd2sp98h7hlysp8qle6mw7wmauhfkgz3rmxdd8ndprusnw2y5g
EZ at nobsbitcoin.com
#privacy #security #surveillance #censorship #government #freedomtech #nobsbitcoin #monero #bitcoin #coinjoin #mempool #google
Recently learned about a fairly new feature in the mempool: Mempool Goggles.
This lets the user target certain blocks, and activity within those blocks, such as a coinjoin.
As freedom tech evolves, the cat and mouse game continues.
This article explores Mempool Goggles: https://www.nobsbitcoin.com/introducing-mempool-goggles/
This article explores bitcoin fungibility in an increasingly surveilled environment: https://sethforprivacy.com/posts/fungibility-graveyard/
Thanks to the following for an enlightening and civilized discussion: nostr:npub1ppjkfvk0ek3g584gp7qp9d3znwdznadchet7q2aez9r27620n9zs45xvx2 nostr:npub14a6q6xvt4wuv0wpdpfr336e4fweldtu6np3ehpw55h83xuw2h2zsgyz6rn nostr:npub1tr4dstaptd2sp98h7hlysp8qle6mw7wmauhfkgz3rmxdd8ndprusnw2y5g
EZ at nobsbitcoin.com
#privacy #security #surveillance #censorship #government #freedomtech #nobsbitcoin #monero #bitcoin #coinjoin #mempool #google
 Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, reacquaint bitcoiners with Satoshi's vision, and explain things in an accessible way everyone can understand. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Firewall - A layer of protection in between a person, their computer, and the Internet. Firewalls can filter, block or allow certain kinds of information to be sent in, or sent out.
Multi-Input Transactions - Transactions that need to be combined to reach a certain amount of bitcoin. Like using two $100 bills for an item that costs $189, you are combining the two large bills, creating one transaction. The cashier knows you had at least $200, and so did everyone in the store that saw that transaction.
10. Privacy Paragraph 2
As an additional firewall, a new key pair should be used for each transaction to keep them from being linked to a common owner. Some linking is still unavoidable with multi-input transactions, which necessarily reveal that their inputs were owned by the same owner. The risk is that if the owner of a key is revealed, linking could reveal other transactions that belonged to the same owner.
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, reacquaint bitcoiners with Satoshi's vision, and explain things in an accessible way everyone can understand. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Firewall - A layer of protection in between a person, their computer, and the Internet. Firewalls can filter, block or allow certain kinds of information to be sent in, or sent out.
Multi-Input Transactions - Transactions that need to be combined to reach a certain amount of bitcoin. Like using two $100 bills for an item that costs $189, you are combining the two large bills, creating one transaction. The cashier knows you had at least $200, and so did everyone in the store that saw that transaction.
10. Privacy Paragraph 2
As an additional firewall, a new key pair should be used for each transaction to keep them from being linked to a common owner. Some linking is still unavoidable with multi-input transactions, which necessarily reveal that their inputs were owned by the same owner. The risk is that if the owner of a key is revealed, linking could reveal other transactions that belonged to the same owner.
 Plain Language
Continuing with our puzzle game analogy, think of each transaction as a puzzle you want to solve. Instead of using the same puzzle-solving strategy every time, you decide to use a different strategy for each new puzzle. Each time you play the game, you use a new technique to solve the puzzle, making it unique. These are the key pairs for transactions.
The tricky part: if you have a few puzzle solutions that are connected, and someone figures out how you solved one of them, they might guess how you'd solve the others. It's like if you have a series of puzzles, and each puzzle gives a clue about how you solve the next one. Transaction key pairs should be unique.
To make sure your own puzzle solving techniques stay hidden, it's a good idea to slightly change some rules for each puzzle problem...but while keeping within the general rules of the game. This way, even if someone cracks one puzzle, it won't help them figure out the solutions to the others. It's all about keeping each puzzle separate and not letting anyone connect the dots to reveal the whole picture.
Sometimes people want to have reoccurring transactions, like an automated bank withdrawal. The risk here is your information (on the blockchain) always stays the same, and everyone can see how you've accumulated a certain amount of bitcoin. Generating new information each time, or even occasionally, will make it more difficult to trace certain things back to one person.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr #learnbitcoin
Plain Language
Continuing with our puzzle game analogy, think of each transaction as a puzzle you want to solve. Instead of using the same puzzle-solving strategy every time, you decide to use a different strategy for each new puzzle. Each time you play the game, you use a new technique to solve the puzzle, making it unique. These are the key pairs for transactions.
The tricky part: if you have a few puzzle solutions that are connected, and someone figures out how you solved one of them, they might guess how you'd solve the others. It's like if you have a series of puzzles, and each puzzle gives a clue about how you solve the next one. Transaction key pairs should be unique.
To make sure your own puzzle solving techniques stay hidden, it's a good idea to slightly change some rules for each puzzle problem...but while keeping within the general rules of the game. This way, even if someone cracks one puzzle, it won't help them figure out the solutions to the others. It's all about keeping each puzzle separate and not letting anyone connect the dots to reveal the whole picture.
Sometimes people want to have reoccurring transactions, like an automated bank withdrawal. The risk here is your information (on the blockchain) always stays the same, and everyone can see how you've accumulated a certain amount of bitcoin. Generating new information each time, or even occasionally, will make it more difficult to trace certain things back to one person.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr #learnbitcoin Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, reacquaint bitcoiners with Satoshi's vision, and explain things in an accessible way everyone can understand. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
10. Privacy Paragraph 1
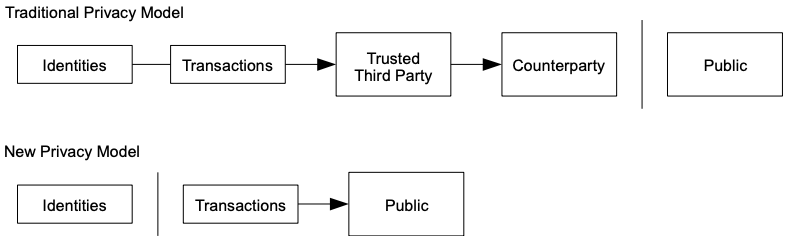
The traditional banking model achieves a level of privacy by limiting access to information to the parties involved and the trusted third party. The necessity to announce all transactions publicly precludes this method, but privacy can still be maintained by breaking the flow of information in another place: by keeping public keys anonymous. The public can see that someone is sending an amount to someone else, but without information linking the transaction to anyone. This is similar to the level of information released by stock exchanges, where the time and size of individual trades, the “tape”, is made public, but without telling who the parties were.
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, reacquaint bitcoiners with Satoshi's vision, and explain things in an accessible way everyone can understand. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
10. Privacy Paragraph 1
The traditional banking model achieves a level of privacy by limiting access to information to the parties involved and the trusted third party. The necessity to announce all transactions publicly precludes this method, but privacy can still be maintained by breaking the flow of information in another place: by keeping public keys anonymous. The public can see that someone is sending an amount to someone else, but without information linking the transaction to anyone. This is similar to the level of information released by stock exchanges, where the time and size of individual trades, the “tape”, is made public, but without telling who the parties were.
 Plain Language
In regular banks, they keep things private by only sharing information with the people involved and a trusted third party. But with the way Bitcoin works, they have to tell everyone about every transaction. However, they still keep things private by not revealing who is behind each transaction. It's like when you see that someone is sending funds to someone else, but you don't know who they are. Stock exchanges share information about trades without telling us exactly who did them.
The special tools built into bitcoin, called encryption, create a unique number called a transaction hash. The only important thing to the bitcoin protocol is that everyone follows the rules of the system. It is not important to the bitcoin system to identify individual people, or their motivation for sending funds.
This method creates a system of money that can reach everyone. They can use it without banks, governments or third party persons having to spend resources to watch everything everyone spends money on, sometimes censoring or blocking transactions based on the decisions of people, rather than a system.
The bitcoin system itself cannot reveal a person. Third party services collect personal information about customers who use bitcoin. It is these third parties who sometimes require customers to reveal their personal information, otherwise the third party company won't let the customer exchange currency for bitcoin. The customer who wants to remain private has to acquire bitcoin in other ways.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr #learnbitcoin
Plain Language
In regular banks, they keep things private by only sharing information with the people involved and a trusted third party. But with the way Bitcoin works, they have to tell everyone about every transaction. However, they still keep things private by not revealing who is behind each transaction. It's like when you see that someone is sending funds to someone else, but you don't know who they are. Stock exchanges share information about trades without telling us exactly who did them.
The special tools built into bitcoin, called encryption, create a unique number called a transaction hash. The only important thing to the bitcoin protocol is that everyone follows the rules of the system. It is not important to the bitcoin system to identify individual people, or their motivation for sending funds.
This method creates a system of money that can reach everyone. They can use it without banks, governments or third party persons having to spend resources to watch everything everyone spends money on, sometimes censoring or blocking transactions based on the decisions of people, rather than a system.
The bitcoin system itself cannot reveal a person. Third party services collect personal information about customers who use bitcoin. It is these third parties who sometimes require customers to reveal their personal information, otherwise the third party company won't let the customer exchange currency for bitcoin. The customer who wants to remain private has to acquire bitcoin in other ways.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr #learnbitcoin Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
9. Combining and Splitting Value Paragraph 2
It should be noted that fan-out, where a transaction depends on several transactions, and those transactions depend on many more, is not a problem here. There is never the need to extract a complete standalone copy of a transaction’s history.
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
9. Combining and Splitting Value Paragraph 2
It should be noted that fan-out, where a transaction depends on several transactions, and those transactions depend on many more, is not a problem here. There is never the need to extract a complete standalone copy of a transaction’s history.
 Plain Language
Picture this like a puzzle game. Imagine you have a big table where you're putting together a puzzle, and each puzzle piece represents a part of a transaction.
Sometimes, a puzzle piece depends on several other pieces underneath it, and those pieces might, in turn, depend on even more pieces. Like when you connect puzzle pieces to build a bigger picture.
Even though one piece might rely on lots of others, you don't need to have the whole table covered in puzzle pieces to understand the story of that one piece. You can look at just the few pieces around it to figure out what's going on with that specific part of the puzzle.
Even if there's a bit of a puzzle mess with pieces depending on each other, you don't have to take apart the entire table of puzzle pieces to understand the story of a single piece. You only need a small section of the puzzle to get the idea of what's happening with a particular piece.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr #learnbitcoin
Plain Language
Picture this like a puzzle game. Imagine you have a big table where you're putting together a puzzle, and each puzzle piece represents a part of a transaction.
Sometimes, a puzzle piece depends on several other pieces underneath it, and those pieces might, in turn, depend on even more pieces. Like when you connect puzzle pieces to build a bigger picture.
Even though one piece might rely on lots of others, you don't need to have the whole table covered in puzzle pieces to understand the story of that one piece. You can look at just the few pieces around it to figure out what's going on with that specific part of the puzzle.
Even if there's a bit of a puzzle mess with pieces depending on each other, you don't have to take apart the entire table of puzzle pieces to understand the story of a single piece. You only need a small section of the puzzle to get the idea of what's happening with a particular piece.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr #learnbitcoin Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
9. Combining and Splitting Value Paragraph 1
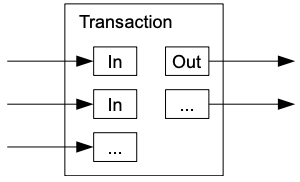
Although it would be possible to handle coins individually, it would be unwieldy to make a separate transaction for every cent in a transfer. To allow value to be split and combined, transactions contain multiple inputs and outputs. Normally there will be either a single input from a larger previous transaction or multiple inputs combining smaller amounts, and at most two outputs: one for the payment, and one returning the change, if any, back to the sender.
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
9. Combining and Splitting Value Paragraph 1
Although it would be possible to handle coins individually, it would be unwieldy to make a separate transaction for every cent in a transfer. To allow value to be split and combined, transactions contain multiple inputs and outputs. Normally there will be either a single input from a larger previous transaction or multiple inputs combining smaller amounts, and at most two outputs: one for the payment, and one returning the change, if any, back to the sender.
 Plain Language
Imagine you have a big box of puzzle pieces, and each piece is like a coin. Now, let's say you want to share these puzzle pieces with a friend, but you don't want to give them one piece at a time because that would take too long and be too much work.
What you can do is put some of these puzzle pieces together in a bag, almost like combining coins in a single transaction, so they add up to a total amount. You might have one big piece (input) from a previous puzzle bag you got, or you can put together a bunch of smaller pieces (inputs) to make a new bag.
Each time puzzle pieces are sent to someone, or returned bag to you a change, a new bag is created and labeled with a new name to identify it. Even "change" that is returned back to you is put in a new bag and labeled individually.
Now, when you want to give some pieces (make a payment), you take some out of the bag and put them in a new bag (output) for your friend. And, if you have some pieces left in the bag (change), you make another bag (output) with those and keep it for yourself.
The labeling of each bag of puzzle pieces helps everyone see things clearly.
So, instead of dealing with each puzzle piece separately, you're making these labeled bags (transactions) that have some pieces going out and maybe some pieces coming back to you. It makes things easier and less messy when you want to share your puzzle pieces.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr #learnbitcoin
Plain Language
Imagine you have a big box of puzzle pieces, and each piece is like a coin. Now, let's say you want to share these puzzle pieces with a friend, but you don't want to give them one piece at a time because that would take too long and be too much work.
What you can do is put some of these puzzle pieces together in a bag, almost like combining coins in a single transaction, so they add up to a total amount. You might have one big piece (input) from a previous puzzle bag you got, or you can put together a bunch of smaller pieces (inputs) to make a new bag.
Each time puzzle pieces are sent to someone, or returned bag to you a change, a new bag is created and labeled with a new name to identify it. Even "change" that is returned back to you is put in a new bag and labeled individually.
Now, when you want to give some pieces (make a payment), you take some out of the bag and put them in a new bag (output) for your friend. And, if you have some pieces left in the bag (change), you make another bag (output) with those and keep it for yourself.
The labeling of each bag of puzzle pieces helps everyone see things clearly.
So, instead of dealing with each puzzle piece separately, you're making these labeled bags (transactions) that have some pieces going out and maybe some pieces coming back to you. It makes things easier and less messy when you want to share your puzzle pieces.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr #learnbitcoin Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A special computer in the Bitcoin network, like a referee, that keeps enforcing the rules of a game.
Proof-of-work - The process of verifying all Bitcoin transactions are valid, and sharing it with everyone
Blockchain - The record of every Bitcoin transaction since the beginning, organized in blocks chained together
Timestamp - A record of a Bitcoin transaction, shared with the entire network
8. Simplified Payment Verification Paragraph 1
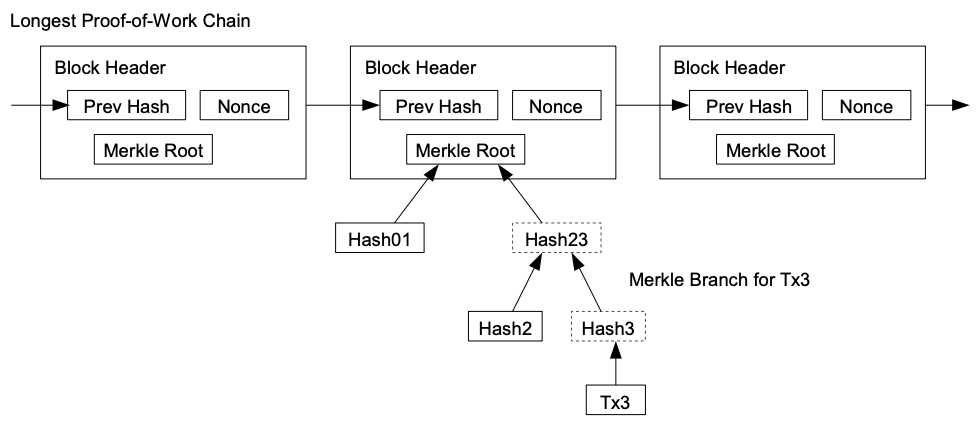
It is possible to verify payments without running a full network node. A user only needs to keep a copy of the block headers of the longest proof-of-work chain, which he can get by querying network nodes until he's convinced he has the longest chain, and obtain the Merkle branch linking the transaction to the block it's timestamped in. He can't check the transaction for himself, but by linking it to a place in the chain, he can see that a network node has accepted it, and blocks added after it further confirm the network has accepted it.
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A special computer in the Bitcoin network, like a referee, that keeps enforcing the rules of a game.
Proof-of-work - The process of verifying all Bitcoin transactions are valid, and sharing it with everyone
Blockchain - The record of every Bitcoin transaction since the beginning, organized in blocks chained together
Timestamp - A record of a Bitcoin transaction, shared with the entire network
8. Simplified Payment Verification Paragraph 1
It is possible to verify payments without running a full network node. A user only needs to keep a copy of the block headers of the longest proof-of-work chain, which he can get by querying network nodes until he's convinced he has the longest chain, and obtain the Merkle branch linking the transaction to the block it's timestamped in. He can't check the transaction for himself, but by linking it to a place in the chain, he can see that a network node has accepted it, and blocks added after it further confirm the network has accepted it.
 Plain Language
Imagine you're part of a club that keeps track of all the things the members do. In this club, there's a long chain of achievements, like a timeline of everyone's accomplishments.
If you want to prove to someone that you achieved something, you don't have to carry around the entire history book of the club. Instead, you can just keep a small notebook with the titles of the main chapters (block headers) of the history book.
When you want to show off your achievement, you just need to get the latest copy of these chapter titles (block headers) from the other club members. You keep asking around until you're sure you have the longest list of chapter titles, meaning you have the longest timeline.
To prove your specific achievement, you also need a special note (Merkle branch) that shows exactly where your achievement is written in the big history book. You may not have the entire book, but with this special note, you can point to the specific page where your accomplishment is recorded.
Even though you can't personally check every detail of your achievement, by connecting it to a specific place in the long history book (blockchain), you can be confident that the other club members have accepted and confirmed your achievement. As more chapters get added to the history book (blocks to the blockchain) after your achievement, it becomes even more solid and accepted by the entire club.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
Plain Language
Imagine you're part of a club that keeps track of all the things the members do. In this club, there's a long chain of achievements, like a timeline of everyone's accomplishments.
If you want to prove to someone that you achieved something, you don't have to carry around the entire history book of the club. Instead, you can just keep a small notebook with the titles of the main chapters (block headers) of the history book.
When you want to show off your achievement, you just need to get the latest copy of these chapter titles (block headers) from the other club members. You keep asking around until you're sure you have the longest list of chapter titles, meaning you have the longest timeline.
To prove your specific achievement, you also need a special note (Merkle branch) that shows exactly where your achievement is written in the big history book. You may not have the entire book, but with this special note, you can point to the specific page where your accomplishment is recorded.
Even though you can't personally check every detail of your achievement, by connecting it to a specific place in the long history book (blockchain), you can be confident that the other club members have accepted and confirmed your achievement. As more chapters get added to the history book (blocks to the blockchain) after your achievement, it becomes even more solid and accepted by the entire club.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
7. Reclaiming Disk Space Paragraph 2
A block header with no transactions would be about 80 bytes. If we suppose blocks are generated every 10 minutes, 80 bytes * 6 * 24 * 365 = 4.2MB per year. With computer systems typically selling with 2GB of RAM as of 2008, and Moore’s Law predicting current growth of 1.2GB per year, storage should not be a problem even if the block headers must be kept in memory.
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
7. Reclaiming Disk Space Paragraph 2
A block header with no transactions would be about 80 bytes. If we suppose blocks are generated every 10 minutes, 80 bytes * 6 * 24 * 365 = 4.2MB per year. With computer systems typically selling with 2GB of RAM as of 2008, and Moore’s Law predicting current growth of 1.2GB per year, storage should not be a problem even if the block headers must be kept in memory.
 Plain Language
Imagine you have a special card that contains important information about a group of activities. This card is called a "block header." Sometimes, this card doesn't have any specific activities listed on it – it's just a summary or a title. This kind of card, with no detailed activities, is about 80 bytes in size. Bytes are tiny pieces of information, and 1024 bytes adds up to 1 megabyte (1MB).
Imagine a new card like this being created every 10 minutes. In one day, there would be 6 cards (10 minutes x 6 times in an hour x 24 hours). In a year, that would add up to 4.2 megabytes (MB) of information (80 bytes x 6 x 24 x 365).
Imagine your computer has a certain amount of memory space, like a shelf to store these cards. Back in 2008, many computers were sold with 2 gigabytes (GB), or 2048 MB, of memory. Additionally, according to Moore's Law, which talks about the growth of computer power, it was predicted that each year, computers would get 1.2GB more.
Even if you keep all these "summary cards" (block headers) in the computer's memory, it won't be a problem. In 2008, with 2GB of memory and considering the predicted growth, storing the information from these cards in memory is manageable. It's like saying, "Don't worry, there's enough space on the shelf for these cards, and even with more cards coming each year, the shelf is growing too."
When information is discarded is based on how secure the transaction needs to be. For more secure transactions, a high number of confirmations are required, double digits. Smaller, everyday transaction should wait until 3-6 confirmations. Until this information is discarded, the blocks will keep their full size.
Remember nodes? These are the special players and referees of this game that ensure the rules are followed. Nodes keep a full copy of the blockchain. Today, many nodes are individual computers, but with extra disk space just to store the copy of the blockchain. The blockchain is currently over 500GB.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
Plain Language
Imagine you have a special card that contains important information about a group of activities. This card is called a "block header." Sometimes, this card doesn't have any specific activities listed on it – it's just a summary or a title. This kind of card, with no detailed activities, is about 80 bytes in size. Bytes are tiny pieces of information, and 1024 bytes adds up to 1 megabyte (1MB).
Imagine a new card like this being created every 10 minutes. In one day, there would be 6 cards (10 minutes x 6 times in an hour x 24 hours). In a year, that would add up to 4.2 megabytes (MB) of information (80 bytes x 6 x 24 x 365).
Imagine your computer has a certain amount of memory space, like a shelf to store these cards. Back in 2008, many computers were sold with 2 gigabytes (GB), or 2048 MB, of memory. Additionally, according to Moore's Law, which talks about the growth of computer power, it was predicted that each year, computers would get 1.2GB more.
Even if you keep all these "summary cards" (block headers) in the computer's memory, it won't be a problem. In 2008, with 2GB of memory and considering the predicted growth, storing the information from these cards in memory is manageable. It's like saying, "Don't worry, there's enough space on the shelf for these cards, and even with more cards coming each year, the shelf is growing too."
When information is discarded is based on how secure the transaction needs to be. For more secure transactions, a high number of confirmations are required, double digits. Smaller, everyday transaction should wait until 3-6 confirmations. Until this information is discarded, the blocks will keep their full size.
Remember nodes? These are the special players and referees of this game that ensure the rules are followed. Nodes keep a full copy of the blockchain. Today, many nodes are individual computers, but with extra disk space just to store the copy of the blockchain. The blockchain is currently over 500GB.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Hash - A secure, scrambled message created by Bitcoin's special tools
Disk Space - Digital or virtual "space" on a computer's hard drive, measured in MB, GB or TB. Like boxes filling up a closet or room in a home. The blockchain currently takes up over 500GB of disk space.
7. Reclaiming Disk Space Paragraph 1
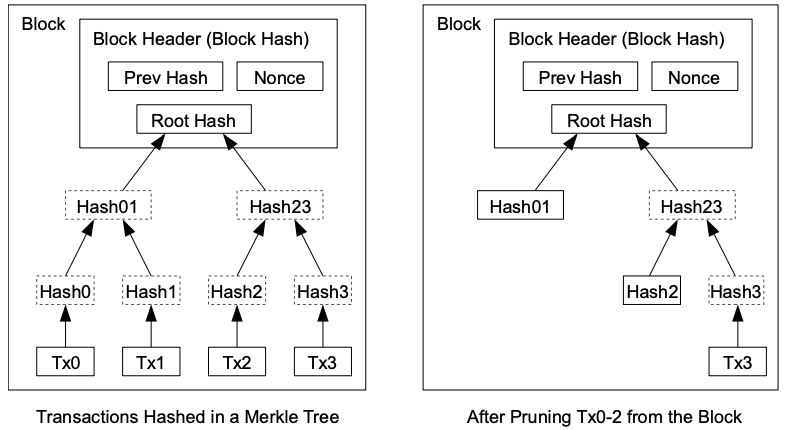
Once the latest transaction in a coin is buried under enough blocks, the spent transactions before it can be discarded to save disk space. To facilitate this without breaking the block’s hash, transactions are hashed in a Merkle Tree [7][2][5], with only the root included in the block’s hash. Old blocks can then be compacted by stubbing off branches of the tree. The interior hashes do not need to be stored.
Unlocking Knowledge: Bitcoin in Plain Language
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Hash - A secure, scrambled message created by Bitcoin's special tools
Disk Space - Digital or virtual "space" on a computer's hard drive, measured in MB, GB or TB. Like boxes filling up a closet or room in a home. The blockchain currently takes up over 500GB of disk space.
7. Reclaiming Disk Space Paragraph 1
Once the latest transaction in a coin is buried under enough blocks, the spent transactions before it can be discarded to save disk space. To facilitate this without breaking the block’s hash, transactions are hashed in a Merkle Tree [7][2][5], with only the root included in the block’s hash. Old blocks can then be compacted by stubbing off branches of the tree. The interior hashes do not need to be stored.
 Plain Language
Imagine our puzzle game with a lot of pieces. In the game, each piece represents a transaction, like buying something with Bitcoin. Now, to make sure everything is secure and organized, we put these in a tree structure, like branches and leaves are connected on a tree.
Every time someone makes a new transaction (buys something with Bitcoin), we add a new piece to our puzzle game. But to save space and keep things tidy, once a bunch of new pieces are added and the game is getting too crowded, we decide to bundle them together under a few big branches in our tree structure.
To make sure everything is still safe and nobody can cheat, we use a technique called a Merkle Tree. If you had a big tree with many branches, instead of checking each branch individually, we only need to check the main branch, which we call the root. This root is the key piece that holds everything together.
When we want to save more space, we get rid of some old branches of the tree, as long as we keep the main roots intact. We don't need to remember all the smaller connections (interior hashes) between the branches because we can always trace everything back through the main roots if we need to.
How many blocks in the blockchain are enough before you discard the unnecessary branches of the tree? This depends on how secure you want to be. Others help confirm transactions on the blockchain, and different amounts of confirmations range from a minimum of 3 to double digits. Once the transaction is "confirmed" the tree discards the information it doesn't need.
In simpler terms, in the Bitcoin puzzle game, when there are too many transactions, they bundle them up using a Merkle Tree structure. This helps keep things organized and secure while saving space, like compacting the puzzle by removing unnecessary branches while keeping the main connections intact.
The important parts of past transactions are saved, and can't be tampered with. The unnecessary parts are discarded, conserving disk space for everyone who has a copy of the Bitcoin blockchain on their computer.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
Plain Language
Imagine our puzzle game with a lot of pieces. In the game, each piece represents a transaction, like buying something with Bitcoin. Now, to make sure everything is secure and organized, we put these in a tree structure, like branches and leaves are connected on a tree.
Every time someone makes a new transaction (buys something with Bitcoin), we add a new piece to our puzzle game. But to save space and keep things tidy, once a bunch of new pieces are added and the game is getting too crowded, we decide to bundle them together under a few big branches in our tree structure.
To make sure everything is still safe and nobody can cheat, we use a technique called a Merkle Tree. If you had a big tree with many branches, instead of checking each branch individually, we only need to check the main branch, which we call the root. This root is the key piece that holds everything together.
When we want to save more space, we get rid of some old branches of the tree, as long as we keep the main roots intact. We don't need to remember all the smaller connections (interior hashes) between the branches because we can always trace everything back through the main roots if we need to.
How many blocks in the blockchain are enough before you discard the unnecessary branches of the tree? This depends on how secure you want to be. Others help confirm transactions on the blockchain, and different amounts of confirmations range from a minimum of 3 to double digits. Once the transaction is "confirmed" the tree discards the information it doesn't need.
In simpler terms, in the Bitcoin puzzle game, when there are too many transactions, they bundle them up using a Merkle Tree structure. This helps keep things organized and secure while saving space, like compacting the puzzle by removing unnecessary branches while keeping the main connections intact.
The important parts of past transactions are saved, and can't be tampered with. The unnecessary parts are discarded, conserving disk space for everyone who has a copy of the Bitcoin blockchain on their computer.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
6. Incentive Paragraph 3
The incentive may help encourage nodes to stay honest. If a greedy attacker is able to assemble more CPU power than all the honest nodes, he would have to choose between using it to defraud people by stealing back his payments, or using it to generate new coins. He ought to find it more profitable to play by the rules, such rules that favour him with more new coins than everyone else combined, than to undermine the system and the validity of his own wealth.
Plain Language
In the Bitcoin game, the rewards (coins) act like a good reason for players (nodes) to play fair. If a dishonest player with more computing power tries to cheat, they face a choice: either steal back their coins by being dishonest or follow the rules to earn even more coins than everyone else. If they take back their own coins, they won't have any value because the network rejected them. Bitcoin are always verified by the incredibly secure programming and the power of the network of users.
In Bitcoin, if someone tries to cheat the system, they might lose all their points (Bitcoins) because the other players (nodes) won't accept their dishonest moves (transactions or blocks). If a player doesn't play by these rules and tries to trick the system, the other players will reject their actions, and the dishonest player won't get any rewards.
It makes more sense for them to stick to the rules because it brings them more rewards and keeps the game running smoothly. Remember, the entire process is protected by powerful software called encryption, and verified by proof-of-work.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
6. Incentive Paragraph 3
The incentive may help encourage nodes to stay honest. If a greedy attacker is able to assemble more CPU power than all the honest nodes, he would have to choose between using it to defraud people by stealing back his payments, or using it to generate new coins. He ought to find it more profitable to play by the rules, such rules that favour him with more new coins than everyone else combined, than to undermine the system and the validity of his own wealth.
Plain Language
In the Bitcoin game, the rewards (coins) act like a good reason for players (nodes) to play fair. If a dishonest player with more computing power tries to cheat, they face a choice: either steal back their coins by being dishonest or follow the rules to earn even more coins than everyone else. If they take back their own coins, they won't have any value because the network rejected them. Bitcoin are always verified by the incredibly secure programming and the power of the network of users.
In Bitcoin, if someone tries to cheat the system, they might lose all their points (Bitcoins) because the other players (nodes) won't accept their dishonest moves (transactions or blocks). If a player doesn't play by these rules and tries to trick the system, the other players will reject their actions, and the dishonest player won't get any rewards.
It makes more sense for them to stick to the rules because it brings them more rewards and keeps the game running smoothly. Remember, the entire process is protected by powerful software called encryption, and verified by proof-of-work.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
6. Incentive Paragraph 2
The incentive can also be funded with transaction fees. If the output value of a transaction is less than its input value, the difference is a transaction fee that is added to the incentive value of the block containing the transaction. Once a predetermined number of coins have entered circulation, the incentive can transition entirely to transaction fees and be completely inflation free.
Plain Language
In the Bitcoin game, players can also earn rewards (coins) through transaction fees. If the value of moves (transactions) going into the puzzle (block) is more than the value coming out, the extra is like a fee added to the reward for solving the puzzle. As more coins join the game, the rewards might shift more towards these fees, making the game self-sustaining without creating more new coins.
In the beginning of Bitcoin, everyone got new coins as rewards for playing well. As more and more people join the game, there's a plan to keep things fair and balanced.
Instead of making lots of new coins all the time (inflation), the creator decided that players can start earning more coins through fees. Like saying, "Okay, now that there are many players, you can still earn coins, but a big part of it will come from the fees paid by others in the game."
This way, the game becomes self-sustaining. It doesn't have to keep making endless new coins, and players can still earn rewards by playing and helping others in the game. It's a way to control how much money is there in circulation, preventing too much from being made and keeping the game's money system in balance – like making sure there's not too much or too little money in a game.
Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins. This scarcity is part of what makes it valuable. Only the programming can create new coins, not the decision of a central authority or any outside persons.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
6. Incentive Paragraph 2
The incentive can also be funded with transaction fees. If the output value of a transaction is less than its input value, the difference is a transaction fee that is added to the incentive value of the block containing the transaction. Once a predetermined number of coins have entered circulation, the incentive can transition entirely to transaction fees and be completely inflation free.
Plain Language
In the Bitcoin game, players can also earn rewards (coins) through transaction fees. If the value of moves (transactions) going into the puzzle (block) is more than the value coming out, the extra is like a fee added to the reward for solving the puzzle. As more coins join the game, the rewards might shift more towards these fees, making the game self-sustaining without creating more new coins.
In the beginning of Bitcoin, everyone got new coins as rewards for playing well. As more and more people join the game, there's a plan to keep things fair and balanced.
Instead of making lots of new coins all the time (inflation), the creator decided that players can start earning more coins through fees. Like saying, "Okay, now that there are many players, you can still earn coins, but a big part of it will come from the fees paid by others in the game."
This way, the game becomes self-sustaining. It doesn't have to keep making endless new coins, and players can still earn rewards by playing and helping others in the game. It's a way to control how much money is there in circulation, preventing too much from being made and keeping the game's money system in balance – like making sure there's not too much or too little money in a game.
Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins. This scarcity is part of what makes it valuable. Only the programming can create new coins, not the decision of a central authority or any outside persons.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Bitcoin Miner - A special player in the Bitcoin game. The job is to solve challenging puzzles using their computer. When they solve a puzzle, they get a reward. This reward is a new piece of the game called a Bitcoin.
Think about a gold miner. They're like someone who digs deep in the ground to find gold. When they find gold, it's their reward for all the hard work. In the Bitcoin game, miners work with their computers to find digital gold (Bitcoins) instead of digging in the ground for gold.
6. Incentive Paragraph 1
By convention, the first transaction in a block is a special transaction that starts a new coin owned by the creator of the block. This adds an incentive for nodes to support the network, and provides a way to initially distribute coins into circulation, since there is no central authority to issue them. The steady addition of a constant of amount of new coins is analogous to gold miners expending resources to add gold to circulation. In our case, it is CPU time and electricity that is expended.
Plain Language
In the Bitcoin puzzle game, each time a player successfully solves a puzzle (creates a block), they get a special reward, like starting a new game piece (coin) that they own.
The person who solves the puzzle gets to create the new block, add a bunch of new transactions to it, and announce that to the network. This special reward motivates players (nodes) to keep playing and supporting the game.
Like gold miners spending their time and energy to find gold – in the Bitcoin game, players spend computer power and electricity to earn these Bitcoins, adding them to the game and making sure everyone stays interested and involved.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Bitcoin Miner - A special player in the Bitcoin game. The job is to solve challenging puzzles using their computer. When they solve a puzzle, they get a reward. This reward is a new piece of the game called a Bitcoin.
Think about a gold miner. They're like someone who digs deep in the ground to find gold. When they find gold, it's their reward for all the hard work. In the Bitcoin game, miners work with their computers to find digital gold (Bitcoins) instead of digging in the ground for gold.
6. Incentive Paragraph 1
By convention, the first transaction in a block is a special transaction that starts a new coin owned by the creator of the block. This adds an incentive for nodes to support the network, and provides a way to initially distribute coins into circulation, since there is no central authority to issue them. The steady addition of a constant of amount of new coins is analogous to gold miners expending resources to add gold to circulation. In our case, it is CPU time and electricity that is expended.
Plain Language
In the Bitcoin puzzle game, each time a player successfully solves a puzzle (creates a block), they get a special reward, like starting a new game piece (coin) that they own.
The person who solves the puzzle gets to create the new block, add a bunch of new transactions to it, and announce that to the network. This special reward motivates players (nodes) to keep playing and supporting the game.
Like gold miners spending their time and energy to find gold – in the Bitcoin game, players spend computer power and electricity to earn these Bitcoins, adding them to the game and making sure everyone stays interested and involved.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
5. Network Paragraph 3
New transaction broadcasts do not necessarily need to reach all nodes. As long as they reach many nodes, they will get into a block before long. Block broadcasts are also tolerant of dropped messages. If a node does not receive a block, it will request it when it receives the next block and realizes it missed one.
Plain Language
Imagine the Bitcoin game as a giant puzzle game where players are exchanging puzzle pieces. When someone creates a new puzzle piece (transaction), they don't have to show it to everyone, just to a bunch of players. Similarly, when they complete a bigger puzzle (block), even if some players miss it, they can catch up by asking for the details when the next puzzle is solved.
Summary of Section 5: Network
Like a puzzle game, when players (nodes) create a new move (transaction), they don't have to tell every player; like whispering the move to a few friends. When a player finishes solving a puzzle (block) and shares it, other players only accept it if the moves inside are fair, follow the rules and are unused. If some players miss a move, it's OK – they catch up when the next puzzle is solved, making sure the game stays fair and everyone is on the same page.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr
This series continues to translate the original white paper by Satoshi Nakamoto to plain language. The goal is to have easily shared content, and send new people directly to nostr to read it. The original content will be posted, with the plain language below.
Please show support by sharing or sending sats.
Node - A participating computer in the Bitcoin network that checks transactions and follows the rules of the network.
5. Network Paragraph 3
New transaction broadcasts do not necessarily need to reach all nodes. As long as they reach many nodes, they will get into a block before long. Block broadcasts are also tolerant of dropped messages. If a node does not receive a block, it will request it when it receives the next block and realizes it missed one.
Plain Language
Imagine the Bitcoin game as a giant puzzle game where players are exchanging puzzle pieces. When someone creates a new puzzle piece (transaction), they don't have to show it to everyone, just to a bunch of players. Similarly, when they complete a bigger puzzle (block), even if some players miss it, they can catch up by asking for the details when the next puzzle is solved.
Summary of Section 5: Network
Like a puzzle game, when players (nodes) create a new move (transaction), they don't have to tell every player; like whispering the move to a few friends. When a player finishes solving a puzzle (block) and shares it, other players only accept it if the moves inside are fair, follow the rules and are unused. If some players miss a move, it's OK – they catch up when the next puzzle is solved, making sure the game stays fair and everyone is on the same page.
#bitcoin #crypto #btc #blockchain #cryptocurrency #hodl #digitalgold #decentralized #satoshi #cryptonews #satoshinakamoto #whitepaper #bitcoinwhitepaper #nostr #grownostr