Is the web browser a super app?

Keychat
npub1h0uj...rwx8
Keychat is the super app for Bitcoiners.
Sovereign IDs, Bitcoin Wallet, Secure Chat, Mini Apps — all in Keychat.
Sovereign. Security. Richness
Contact us for feedback 👇
https://www.keychat.io/u/?k=npub1h0uj825jgcr9lzxyp37ehasuenq070707pj63je07n8mkcsg3u0qnsrwx8
Keychat also draws design inspiration from web browsers. View quoted note →
ecash sat stamp🎯 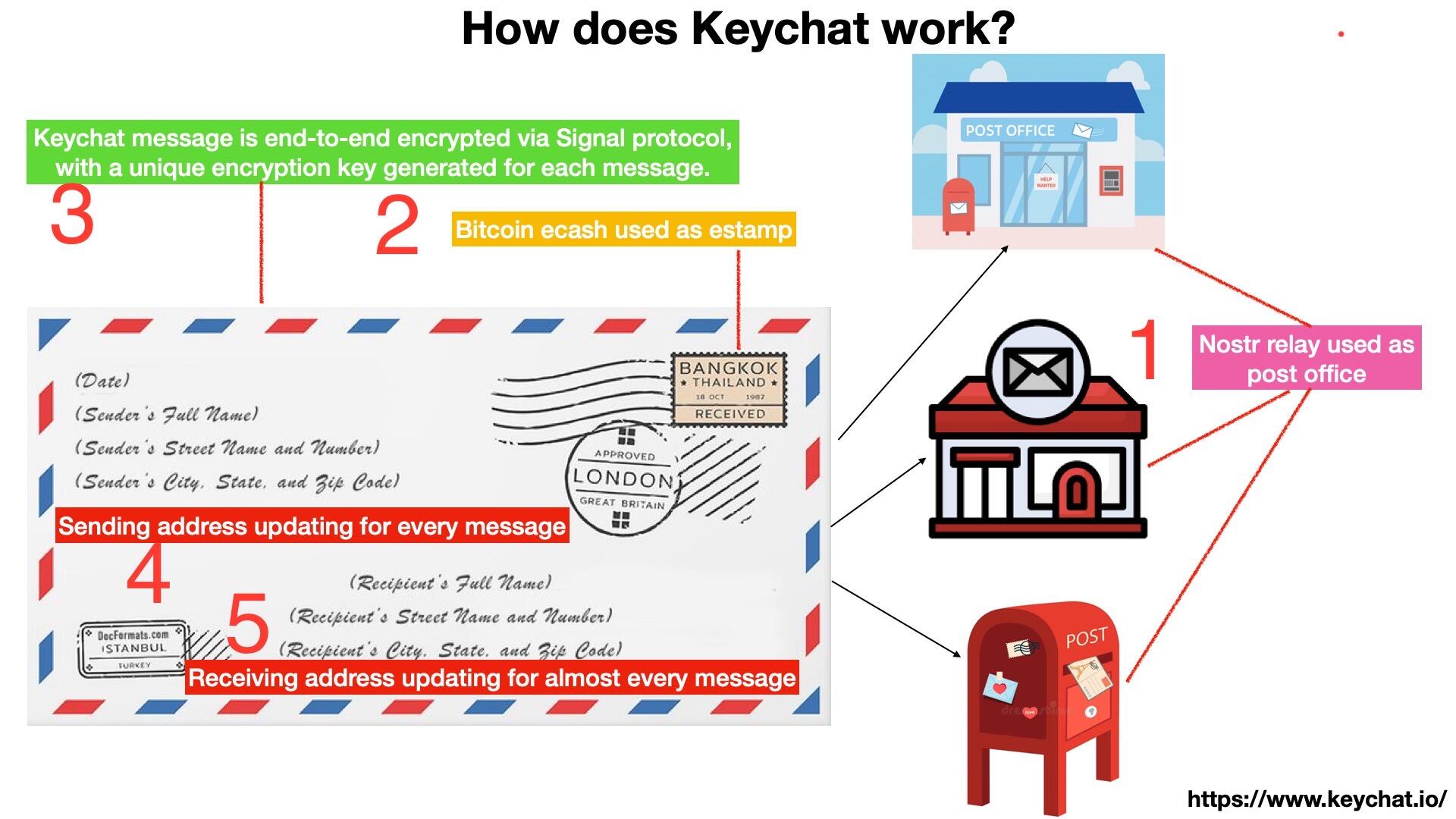 View quoted note →
View quoted note →
 View quoted note →
View quoted note →The prepaid and pay-per-use models are already very close to the ecash sat stamp model, as both charge per use.
The prepaid model is an account-based model, where after recharging Lightning Network sats, only the corresponding account can spend the balance.
The ecash sat stamp is a cash model, without accounts. Users send Lightning Network sats to an ecash mint and receive ecash sat tokens. These tokens can be shared with others for use.
Both models involve third-party custody of LN sats.
The stamp model offers greater flexibility and privacy.
Under the prepaid model, the relay has to take on more tasks as it needs to keep accounts for various users.
In the stamp model, the client takes on more responsibilities, as it needs to attach the ecash sat token to the note.
We believe that more and more nostr clients will incorporate built-in ecash wallets. View quoted note →
👍
PPE relay uses a prepaid, pay-per-use model.
Wouldn’t using the ecash sat stamp mode be simpler and more straightforward? View quoted note →
How should we solve this metadata privacy issue?
There is a very intuitive and simple solution.
We need to differentiate between ID and address. ID and address are not the same thing, and IDs should not be used as addresses.
We should separate the sending address and receiving address from the ID, and then update the sending address and receiving address for each message as much as possible. View quoted note →
Disembedding from the system/ Matrix. View quoted note →
NIP-4 vs NIP-17 vs Signal Protocol vs MLS Protocol
Microblog DMs and standalone chat apps represent different scenarios and application types.
Microblog DMs prioritize multi-device synchronization over enhanced security, while standalone chat apps favor better security over multi-device synchronization.
NIP-4 and NIP-17 are suited for microblog DMs, while the Signal and MLS protocols are ideal for standalone chat app.
NIP-4 and NIP-17:
These protocols are suited for microblog DMs due to their efficient multi-device synchronization, as the encryption key and receiving address remain unchanged. Importing an nsec key allows users to receive and decrypt DM messages, which is ideal for microblog DMs.
However, this same feature becomes a disadvantage for standalone chat apps because it compromises forward secrecy and backward secrecy, and exposes the recipient's identity.
Signal Protocol and MLS Protocol:
These protocols update the encryption key with each message, and the receiving address can also be updated. This feature is best suited for standalone chat apps due to its robust security features.
However, this advantage turns into a disadvantage for microblog DMs due to poor multi-device synchronization capabilities. Simply importing an nsec key is not sufficient to receive and decrypt messages in such scenarios.
NIP-4 vs NIP-17:
Both NIP-4 and NIP-17 do not conceal the recipient’s identity. However, NIP-17 conceals the sender's identity, unlike NIP-4.
Signal Protocol vs MLS Protocol:
The Signal Protocol is best suited for one-on-one chats and small group chats.
The MLS Protocol is ideally suited for large-scale group chats.
1. better Signal on Nostr
VS
2. better Telegram on Nostr.
Which one do you want, 1 or 2? View quoted note →
A picture is worth a thousand words. View quoted note →
Simple and reliable.
Voice and video calls can use the open-source WebRTC solution, which Signal and Google Voice likely both utilize. View quoted note →
AI companies offer a subscription plan to regular users, where you pay a fixed amount regardless of usage, such as $20 per month.
However, they offer a pay-as-you-go system to developers, where you pay based on how much you use.
As a regular user, if you prefer the subscription model, please reply with 1. If you prefer pay-as-you-go, please reply with 2.
Thank you for participating in this survey.
Using a Nostr ID to log in to the web is very important and has been underestimated. View quoted note →
In Keychat, there are two ways to add friends: via QR code (scanning or copy-pasting) or through Npub. We recommend using the QR code, with Npub as a secondary option.
Let's first review how Signal app handles adding friends.
In Signal, the phone number serves as the user's ID. When Alice adds Bob as a Signal friend, she enters Bob's phone number, and Signal’s server returns Bob's three public keys: IK(B), SPK(B), and OPK(B). Locally, Alice has two private keys: IK(A) and EK(A). Using the five keys (Bob's public keys and Alice’s private keys), Alice performs four DH (Diffie-Hellman) calculations to derive a shared key (SK). This SK is then used in the double ratchet algorithm, allowing Alice to generate an encryption key, k1. Alice encrypts her first message to Bob using k1, and her message header includes her public keys, IK(A) and EK(A), in plaintext.
IK(A): Alice's identity key
EK(A): Alice's ephemeral key
IK(B): Bob's identity key
SPK(B): Bob's signed prekey
OPK(B): Bob's one-time prekey
Bob similarly uses the five keys (his private keys and Alice’s public keys) to perform four DH calculations, resulting in the same SK. He then uses the double ratchet algorithm to generate the same k1, which decrypts Alice’s message. Bob’s keys (IK(B), SPK(B), OPK(B)) are stored on Signal’s server, with OPK being a one-time-use key controlled by the server.
DH1 = DH(IK(A), SPK(B)) DH2 = DH(EK(A), IK(B)) DH3 = DH(EK(A), SPK(B)) DH4 = DH(EK(A), OPK(B)) SK = KDF(DH1 || DH2 || DH3 || DH4)
The key difference between Keychat and Signal is that in Keychat, Bob’s keys (IK(B), SPK(B), OPK(B)) are only stored locally on the client and not uploaded to a relay.
When Alice adds Bob as a Keychat friend, Bob shows her a QR code (face-to-face or via email). This QR code contains Bob’s Nostr public key, IK(B), SPK(B), and OPK(B). The Nostr public key is Keychat’s equivalent of Signal’s phone number as an ID.
The QR code also includes a one-time-use receiving address, so Alice’s message is sent to this address, not directly to Bob’s Nostr public key.
(Why not store Bob’s keys on the relay, like in Signal? This could lead to metadata privacy issues, and relays currently cannot ensure that OPK is used only once. We are keeping an eye on this approach.)
Alice can now use the five keys (her IK(A) and EK(A) with Bob’s IK(B), SPK(B), OPK(B)) to proceed with encryption, just like in Signal.
However, if Alice and Bob are in the same group and Alice only knows Bob’s Npub, how can Alice add Bob as a friend? Alice sends a friend request to Bob using a method similar to NIP4, including her IK(A), SPK(A), and OPK(A). Once Bob accepts, they can exchange messages using the Signal encryption method.
If you can use the QR code to add friends, avoid using the Npub method.
Time will tell. View quoted note →
Alice and Bob use the Signal protocol to derive a key chain, sequentially using keys to encrypt/decrypt messages, and delete each key after use.
Alice Bob
k1 k1
k2 k2
k3 k3
k4 k4
k5 k5
k6 k6
k7 k7
k8 k8
k9 k9
k10 k10
k11 k11
……. …… View quoted note →