We’ve got a good #DecodingBitcoin post for you today. The topic? 𝐄𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐬𝐬, AKA the order of bytes in a computer’s memory.
When we put it like that it sounds a little boring, but there’s something interesting, and dare we say 𝑎𝑛𝑛𝑜𝑦𝑖𝑛𝑔, about how bitcoin handles endianness…
Before we get to that, let’s better understand what endianness is.
Imagine reading directions in different languages: while English is written and read from left to right, Arabic text flows from right to left.
 Similarly, computers have two ways to store data:
1. 𝐁𝐢𝐠-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 (BE): Most significant byte first
2. 𝐋𝐢𝐭𝐭𝐥𝐞-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 (LE): Least significant byte first
Similarly, computers have two ways to store data:
1. 𝐁𝐢𝐠-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 (BE): Most significant byte first
2. 𝐋𝐢𝐭𝐭𝐥𝐞-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 (LE): Least significant byte first
 When computers with different byte orders try to communicate, they can misread each other. It’s like two people reading numbers from opposite directions.
When computers with different byte orders try to communicate, they can misread each other. It’s like two people reading numbers from opposite directions.
 𝐁𝐢𝐠-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 𝐟𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭. This is similar to how humans read numbers and Hex in most cases: starting with the most important information.
Suppose we want to store the number 12345678 (hexadecimal: 0x00BC614E) in memory. In big-endian, the bytes are stored in this order:
00 BC 61 4E
𝐁𝐢𝐠-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 𝐟𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭. This is similar to how humans read numbers and Hex in most cases: starting with the most important information.
Suppose we want to store the number 12345678 (hexadecimal: 0x00BC614E) in memory. In big-endian, the bytes are stored in this order:
00 BC 61 4E
 Observe that:
- The 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (00) is stored at the 𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐦𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (00).
- The 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (4E) is stored at the 𝐡𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (03).
Big-endian is considered more "human-readable" because the data is stored in the order we naturally read it.
𝐋𝐢𝐭𝐭𝐥𝐞-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 𝐟𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭. This might feel counter intuitive to humans but is more efficient for modern processors.
Using the same number 12345678 (0x00BC614E), here's how it looks in little-endian:
4E 61 BC 00
Observe that:
- The 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (00) is stored at the 𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐦𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (00).
- The 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (4E) is stored at the 𝐡𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (03).
Big-endian is considered more "human-readable" because the data is stored in the order we naturally read it.
𝐋𝐢𝐭𝐭𝐥𝐞-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 𝐟𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭. This might feel counter intuitive to humans but is more efficient for modern processors.
Using the same number 12345678 (0x00BC614E), here's how it looks in little-endian:
4E 61 BC 00
 This time, the 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (4E) is stored at the 𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐦𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (00).
The 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (00) is stored at the 𝐡𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (03).
This "reversal" of bytes is common in the Bitcoin Core codebase.
In bitcoin, most data like transaction IDs, block headers, and amounts are all in little-endian format or with the bytes reversed.
This time, the 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (4E) is stored at the 𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐦𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (00).
The 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (00) is stored at the 𝐡𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (03).
This "reversal" of bytes is common in the Bitcoin Core codebase.
In bitcoin, most data like transaction IDs, block headers, and amounts are all in little-endian format or with the bytes reversed.
 𝑁𝑜𝑡𝑒: 𝐸𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑛𝑙𝑦 𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑒𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑔𝑒𝑟𝑠. 𝐼𝑡 𝑖𝑠 𝑛𝑜𝑡 𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝑠𝑎𝑦 𝑎 ℎ𝑎𝑠ℎ 𝑖𝑠 𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑙𝑒-𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛. 𝑆𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒’𝑠 𝑛𝑜 𝑜𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑡ℎ𝑖𝑠 𝑤𝑒 𝑠𝑎𝑦 “𝑏𝑦𝑡𝑒 𝑠𝑤𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑒𝑑” 𝑜𝑟 “𝑟𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑒 𝑏𝑦𝑡𝑒𝑠”.
For readability, the bytes are swapped back to the style of big-endian when this data is displayed to humans. A block explorer is one example of where you can see this.
Bitcoin Core’s JSON-RPC interface was the first time block hashes were printed for human consumption. That was when someone decided to reverse the ordering of hash so that it looked like a human readable integer.
𝑁𝑜𝑡𝑒: 𝐸𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑛𝑙𝑦 𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑒𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑔𝑒𝑟𝑠. 𝐼𝑡 𝑖𝑠 𝑛𝑜𝑡 𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝑠𝑎𝑦 𝑎 ℎ𝑎𝑠ℎ 𝑖𝑠 𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑙𝑒-𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛. 𝑆𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒’𝑠 𝑛𝑜 𝑜𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑡ℎ𝑖𝑠 𝑤𝑒 𝑠𝑎𝑦 “𝑏𝑦𝑡𝑒 𝑠𝑤𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑒𝑑” 𝑜𝑟 “𝑟𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑒 𝑏𝑦𝑡𝑒𝑠”.
For readability, the bytes are swapped back to the style of big-endian when this data is displayed to humans. A block explorer is one example of where you can see this.
Bitcoin Core’s JSON-RPC interface was the first time block hashes were printed for human consumption. That was when someone decided to reverse the ordering of hash so that it looked like a human readable integer.
 It turns out the real block hash, the actual sha256 value you get if you compute the hash yourself, is:
e4b1d56439d46d9070e58c4368cccc97596fa908daf101000000000000000000
The zeros are actually on the right! At first glance it looks like this is a very large number, but we know the integer value of a block hash actually gets smaller as the difficulty increases.
It's clear that the bytes are reversed and in the style of little-endian. But why? We can thank Satoshi for that. Satoshi decided to interpret the block hash as a little-endian integer. The more zeroes there are on the right side, the smaller the (little-endian) integer.
Since most modern CPUs are little-endian, bitcoin uses it to optimize performance.
However, network protocols typically use big-endian, creating a mismatch 🙀
Big-endian is used for network communication (network byte order). Little-endian is used for bitcoin’s internal storage.
This duality requires developers to frequently, and sometimes frustratingly, convert between the two formats when working with bitcoin data.
Have you been the victim of an endianness oversight when writing bitcoin code? It's a common source of pain for developers new to bitcoin (and even the seasoned ones!)
As covered by the transaction ID example earlier, byte order confusion can be common.
It turns out the real block hash, the actual sha256 value you get if you compute the hash yourself, is:
e4b1d56439d46d9070e58c4368cccc97596fa908daf101000000000000000000
The zeros are actually on the right! At first glance it looks like this is a very large number, but we know the integer value of a block hash actually gets smaller as the difficulty increases.
It's clear that the bytes are reversed and in the style of little-endian. But why? We can thank Satoshi for that. Satoshi decided to interpret the block hash as a little-endian integer. The more zeroes there are on the right side, the smaller the (little-endian) integer.
Since most modern CPUs are little-endian, bitcoin uses it to optimize performance.
However, network protocols typically use big-endian, creating a mismatch 🙀
Big-endian is used for network communication (network byte order). Little-endian is used for bitcoin’s internal storage.
This duality requires developers to frequently, and sometimes frustratingly, convert between the two formats when working with bitcoin data.
Have you been the victim of an endianness oversight when writing bitcoin code? It's a common source of pain for developers new to bitcoin (and even the seasoned ones!)
As covered by the transaction ID example earlier, byte order confusion can be common.
 Another gotcha is length specification. When converting to little-endian, always specify the correct byte length:
Another gotcha is length specification. When converting to little-endian, always specify the correct byte length:
 Hope you learned something new about endianness today. If you enjoyed this, share it with a friend and don’t forget to follow us, @Bitcoin Dev Project !
This material is from Decoding Bitcoin, your go-to resource for understanding #bitcoin, privacy, and decentralization.
Visit
Hope you learned something new about endianness today. If you enjoyed this, share it with a friend and don’t forget to follow us, @Bitcoin Dev Project !
This material is from Decoding Bitcoin, your go-to resource for understanding #bitcoin, privacy, and decentralization.
Visit  for the full lesson, and more free, interactive content.
Thanks for reading!
for the full lesson, and more free, interactive content.
Thanks for reading!
 Similarly, computers have two ways to store data:
1. 𝐁𝐢𝐠-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 (BE): Most significant byte first
2. 𝐋𝐢𝐭𝐭𝐥𝐞-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 (LE): Least significant byte first
Similarly, computers have two ways to store data:
1. 𝐁𝐢𝐠-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 (BE): Most significant byte first
2. 𝐋𝐢𝐭𝐭𝐥𝐞-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 (LE): Least significant byte first
 When computers with different byte orders try to communicate, they can misread each other. It’s like two people reading numbers from opposite directions.
When computers with different byte orders try to communicate, they can misread each other. It’s like two people reading numbers from opposite directions.
 𝐁𝐢𝐠-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 𝐟𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭. This is similar to how humans read numbers and Hex in most cases: starting with the most important information.
Suppose we want to store the number 12345678 (hexadecimal: 0x00BC614E) in memory. In big-endian, the bytes are stored in this order:
00 BC 61 4E
𝐁𝐢𝐠-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 𝐟𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭. This is similar to how humans read numbers and Hex in most cases: starting with the most important information.
Suppose we want to store the number 12345678 (hexadecimal: 0x00BC614E) in memory. In big-endian, the bytes are stored in this order:
00 BC 61 4E
 Observe that:
- The 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (00) is stored at the 𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐦𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (00).
- The 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (4E) is stored at the 𝐡𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (03).
Big-endian is considered more "human-readable" because the data is stored in the order we naturally read it.
𝐋𝐢𝐭𝐭𝐥𝐞-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 𝐟𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭. This might feel counter intuitive to humans but is more efficient for modern processors.
Using the same number 12345678 (0x00BC614E), here's how it looks in little-endian:
4E 61 BC 00
Observe that:
- The 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (00) is stored at the 𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐦𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (00).
- The 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (4E) is stored at the 𝐡𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (03).
Big-endian is considered more "human-readable" because the data is stored in the order we naturally read it.
𝐋𝐢𝐭𝐭𝐥𝐞-𝐞𝐧𝐝𝐢𝐚𝐧 𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐫𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 𝐟𝐢𝐫𝐬𝐭. This might feel counter intuitive to humans but is more efficient for modern processors.
Using the same number 12345678 (0x00BC614E), here's how it looks in little-endian:
4E 61 BC 00
 This time, the 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (4E) is stored at the 𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐦𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (00).
The 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (00) is stored at the 𝐡𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (03).
This "reversal" of bytes is common in the Bitcoin Core codebase.
In bitcoin, most data like transaction IDs, block headers, and amounts are all in little-endian format or with the bytes reversed.
This time, the 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (4E) is stored at the 𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐦𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (00).
The 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐧𝐢𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐚𝐧𝐭 𝐛𝐲𝐭𝐞 (00) is stored at the 𝐡𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐭 𝐚𝐝𝐝𝐫𝐞𝐬𝐬 (03).
This "reversal" of bytes is common in the Bitcoin Core codebase.
In bitcoin, most data like transaction IDs, block headers, and amounts are all in little-endian format or with the bytes reversed.
 𝑁𝑜𝑡𝑒: 𝐸𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑛𝑙𝑦 𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑒𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑔𝑒𝑟𝑠. 𝐼𝑡 𝑖𝑠 𝑛𝑜𝑡 𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝑠𝑎𝑦 𝑎 ℎ𝑎𝑠ℎ 𝑖𝑠 𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑙𝑒-𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛. 𝑆𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒’𝑠 𝑛𝑜 𝑜𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑡ℎ𝑖𝑠 𝑤𝑒 𝑠𝑎𝑦 “𝑏𝑦𝑡𝑒 𝑠𝑤𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑒𝑑” 𝑜𝑟 “𝑟𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑒 𝑏𝑦𝑡𝑒𝑠”.
For readability, the bytes are swapped back to the style of big-endian when this data is displayed to humans. A block explorer is one example of where you can see this.
Bitcoin Core’s JSON-RPC interface was the first time block hashes were printed for human consumption. That was when someone decided to reverse the ordering of hash so that it looked like a human readable integer.
𝑁𝑜𝑡𝑒: 𝐸𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑛𝑙𝑦 𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑒𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑔𝑒𝑟𝑠. 𝐼𝑡 𝑖𝑠 𝑛𝑜𝑡 𝑐𝑜𝑟𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝑠𝑎𝑦 𝑎 ℎ𝑎𝑠ℎ 𝑖𝑠 𝑙𝑖𝑡𝑡𝑙𝑒-𝑒𝑛𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛. 𝑆𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒’𝑠 𝑛𝑜 𝑜𝑓𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑎𝑙 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑡ℎ𝑖𝑠 𝑤𝑒 𝑠𝑎𝑦 “𝑏𝑦𝑡𝑒 𝑠𝑤𝑎𝑝𝑝𝑒𝑑” 𝑜𝑟 “𝑟𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑒 𝑏𝑦𝑡𝑒𝑠”.
For readability, the bytes are swapped back to the style of big-endian when this data is displayed to humans. A block explorer is one example of where you can see this.
Bitcoin Core’s JSON-RPC interface was the first time block hashes were printed for human consumption. That was when someone decided to reverse the ordering of hash so that it looked like a human readable integer.
 It turns out the real block hash, the actual sha256 value you get if you compute the hash yourself, is:
e4b1d56439d46d9070e58c4368cccc97596fa908daf101000000000000000000
The zeros are actually on the right! At first glance it looks like this is a very large number, but we know the integer value of a block hash actually gets smaller as the difficulty increases.
It's clear that the bytes are reversed and in the style of little-endian. But why? We can thank Satoshi for that. Satoshi decided to interpret the block hash as a little-endian integer. The more zeroes there are on the right side, the smaller the (little-endian) integer.
Since most modern CPUs are little-endian, bitcoin uses it to optimize performance.
However, network protocols typically use big-endian, creating a mismatch 🙀
Big-endian is used for network communication (network byte order). Little-endian is used for bitcoin’s internal storage.
This duality requires developers to frequently, and sometimes frustratingly, convert between the two formats when working with bitcoin data.
Have you been the victim of an endianness oversight when writing bitcoin code? It's a common source of pain for developers new to bitcoin (and even the seasoned ones!)
As covered by the transaction ID example earlier, byte order confusion can be common.
It turns out the real block hash, the actual sha256 value you get if you compute the hash yourself, is:
e4b1d56439d46d9070e58c4368cccc97596fa908daf101000000000000000000
The zeros are actually on the right! At first glance it looks like this is a very large number, but we know the integer value of a block hash actually gets smaller as the difficulty increases.
It's clear that the bytes are reversed and in the style of little-endian. But why? We can thank Satoshi for that. Satoshi decided to interpret the block hash as a little-endian integer. The more zeroes there are on the right side, the smaller the (little-endian) integer.
Since most modern CPUs are little-endian, bitcoin uses it to optimize performance.
However, network protocols typically use big-endian, creating a mismatch 🙀
Big-endian is used for network communication (network byte order). Little-endian is used for bitcoin’s internal storage.
This duality requires developers to frequently, and sometimes frustratingly, convert between the two formats when working with bitcoin data.
Have you been the victim of an endianness oversight when writing bitcoin code? It's a common source of pain for developers new to bitcoin (and even the seasoned ones!)
As covered by the transaction ID example earlier, byte order confusion can be common.
 Another gotcha is length specification. When converting to little-endian, always specify the correct byte length:
Another gotcha is length specification. When converting to little-endian, always specify the correct byte length:
 Hope you learned something new about endianness today. If you enjoyed this, share it with a friend and don’t forget to follow us, @Bitcoin Dev Project !
This material is from Decoding Bitcoin, your go-to resource for understanding #bitcoin, privacy, and decentralization.
Visit
Hope you learned something new about endianness today. If you enjoyed this, share it with a friend and don’t forget to follow us, @Bitcoin Dev Project !
This material is from Decoding Bitcoin, your go-to resource for understanding #bitcoin, privacy, and decentralization.
Visit 
Decoding Bitcoin
Simplifying bitcoin tech to help you learn as efficiently as possible


 UTXOs are unspent transaction outputs. They can be used as inputs for new transactions.
Think of them as "coins" in a wallet, waiting to be spent.
Alice checks her wallet and finds two UTXOs:
UTXOs are unspent transaction outputs. They can be used as inputs for new transactions.
Think of them as "coins" in a wallet, waiting to be spent.
Alice checks her wallet and finds two UTXOs:
 To create a transaction, Alice has to specify exactly which UTXOs to spend.
A UTXO is identified by the transaction it came from, specifically
- the transaction ID and
- an index that says where the UTXO is in the list of transaction outputs
To create a transaction, Alice has to specify exactly which UTXOs to spend.
A UTXO is identified by the transaction it came from, specifically
- the transaction ID and
- an index that says where the UTXO is in the list of transaction outputs
 Wallets usually store this information for you but you can also look it up on the blockchain.
Alice's wallet shows these available UTXOs:
- UTXO #1: 4 BTC (from Transaction 1, Output Index 1)
- UTXO #2: 2 BTC (from Transaction 2, Output Index 0)
Together, they provide enough funds (4 BTC + 2 BTC = 6 BTC) for the payment and any transaction fees.
Now Alice has everything she needs to identify her UTXOs. As she adds them to the transaction, she saves space for the signatures she will make later. These signatures authorize the spending of the UTXOs.
Wallets usually store this information for you but you can also look it up on the blockchain.
Alice's wallet shows these available UTXOs:
- UTXO #1: 4 BTC (from Transaction 1, Output Index 1)
- UTXO #2: 2 BTC (from Transaction 2, Output Index 0)
Together, they provide enough funds (4 BTC + 2 BTC = 6 BTC) for the payment and any transaction fees.
Now Alice has everything she needs to identify her UTXOs. As she adds them to the transaction, she saves space for the signatures she will make later. These signatures authorize the spending of the UTXOs.
 Now that the transaction inputs have been taken care of, it’s time to look at the outputs!
Alice needs to create two outputs:
- 5 BTC to Bob (the payment amount)
- 0.99 BTC back to Alice as change (there is a 0.01 BTC transaction fee)
Now that the transaction inputs have been taken care of, it’s time to look at the outputs!
Alice needs to create two outputs:
- 5 BTC to Bob (the payment amount)
- 0.99 BTC back to Alice as change (there is a 0.01 BTC transaction fee)
 Why do we have to make a separate output for change?
UTXOs must be spent in their entirety. You cannot partially spend a UTXO. Instead, you create a new output that sends the excess amount back to yourself as change.
Why do we have to make a separate output for change?
UTXOs must be spent in their entirety. You cannot partially spend a UTXO. Instead, you create a new output that sends the excess amount back to yourself as change.
 Looks good! The transaction structure is now complete, but it’s not yet valid. Alice must sign it to prove she owns the inputs. We’ll cover that in a future lesson 🙂
Follow us
Looks good! The transaction structure is now complete, but it’s not yet valid. Alice must sign it to prove she owns the inputs. We’ll cover that in a future lesson 🙂
Follow us 

 Here's how to calculate the fee for this transaction:
Here's how to calculate the fee for this transaction: 
 Fees incentivise miners to include transactions in blocks. Without fees, miners would have little reason to put transactions into blocks!
In addition to fees, miners also receive a block reward.
Total miner revenue = fees + block reward
Fees incentivise miners to include transactions in blocks. Without fees, miners would have little reason to put transactions into blocks!
In addition to fees, miners also receive a block reward.
Total miner revenue = fees + block reward
 How do miners decide what transactions go into a block?
The short answer is miners will usually maximize revenue by prioritizing transactions with the highest fee rate (we've got a whole lesson fee rates coming!)
How do miners decide what transactions go into a block?
The short answer is miners will usually maximize revenue by prioritizing transactions with the highest fee rate (we've got a whole lesson fee rates coming!)
 While miners can choose which transactions to include based on fees, there's a minimum threshold, a "minimum relay fee" that must be met just for a transaction to be relayed through the network.
Transactions below this threshold are rejected by nodes. It helps prevent spam and DoS attacks on the network
While miners can choose which transactions to include based on fees, there's a minimum threshold, a "minimum relay fee" that must be met just for a transaction to be relayed through the network.
Transactions below this threshold are rejected by nodes. It helps prevent spam and DoS attacks on the network
 This brings us to an important question: What happens if you submit a transaction with a fee rate above the minimum but still too low for current network conditions?
That transaction could sit in the mempool for hours because the fee rate is too low for the high level of network activity. Even if you met the minimum, there can still be plenty of transactions with higher fee rates than yours, ones that miners will choose first.
This brings us to an important question: What happens if you submit a transaction with a fee rate above the minimum but still too low for current network conditions?
That transaction could sit in the mempool for hours because the fee rate is too low for the high level of network activity. Even if you met the minimum, there can still be plenty of transactions with higher fee rates than yours, ones that miners will choose first.
 At this point, you have two main ways to "unstick" it:
1. RBF (Replace-by-Fee)
2. CPFP (Child Pays for Parent)
--------------------------------
That's all for now! We'll dive deeper into fee rates, RBF, and CPFP in a future post.
This material is from Decoding Bitcoin, your go-to resource for understanding #bitcoin, privacy, and decentralization.
If you enjoyed it, visit
At this point, you have two main ways to "unstick" it:
1. RBF (Replace-by-Fee)
2. CPFP (Child Pays for Parent)
--------------------------------
That's all for now! We'll dive deeper into fee rates, RBF, and CPFP in a future post.
This material is from Decoding Bitcoin, your go-to resource for understanding #bitcoin, privacy, and decentralization.
If you enjoyed it, visit 

 The account model is like your bank statement. Simple to understand and works well with smart contracts. The downside is it's less private and can be vulnerable to replay attacks.
The account model is like your bank statement. Simple to understand and works well with smart contracts. The downside is it's less private and can be vulnerable to replay attacks.
 The UTXO model is like bills in a wallet. UTXOs (unspent transaction outputs) can only be spent once. Each transaction creates new UTXOs, and your balance is the sum of all your unspent UTXOs
The UTXO model is like bills in a wallet. UTXOs (unspent transaction outputs) can only be spent once. Each transaction creates new UTXOs, and your balance is the sum of all your unspent UTXOs
 This model has better privacy, prevents double spending, and allows for parallel transaction processing. The cons are it's more difficult to understand, is harder for complex applications, and requires UTXO management.
Here's a comparison chart of the two models:
This model has better privacy, prevents double spending, and allows for parallel transaction processing. The cons are it's more difficult to understand, is harder for complex applications, and requires UTXO management.
Here's a comparison chart of the two models:
 This material is from Decoding Bitcoin, your go-to resource for understanding #bitcoin, privacy, and decentralization.
If you enjoyed it, visit
This material is from Decoding Bitcoin, your go-to resource for understanding #bitcoin, privacy, and decentralization.
If you enjoyed it, visit 

 What will you learn?
- How to find and decode the hidden message in the genesis block
- Elliptic curve cryptography
- Message signing and verification
- Building a transaction
- Building a block template
- Bitcoin Script
- How the Lightning network works
- And so, so much more!
How is Saving Satoshi different?
- Logged in state to remember your progress
- Ability to share accomplishments publicly
- A real story to motivate you to learn
- Free and Open Source
What will you learn?
- How to find and decode the hidden message in the genesis block
- Elliptic curve cryptography
- Message signing and verification
- Building a transaction
- Building a block template
- Bitcoin Script
- How the Lightning network works
- And so, so much more!
How is Saving Satoshi different?
- Logged in state to remember your progress
- Ability to share accomplishments publicly
- A real story to motivate you to learn
- Free and Open Source
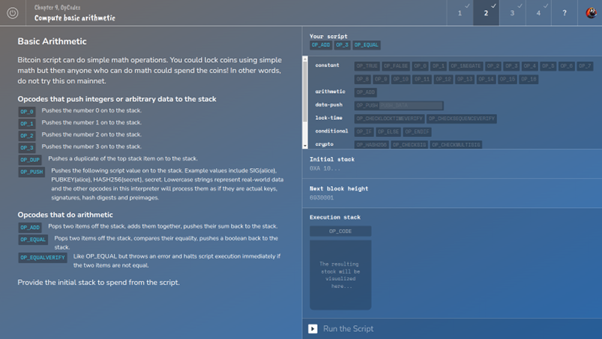 Saving Satoshi started as a hackathon idea:
“How can we make bitcoin tech education more engaging and fun?”
Since then it’s become a game with 10 fun chapters, and support for both Python and JavaScript
Worldwide there are groups like TabConf and Scalar School playing together.
Saving Satoshi started as a hackathon idea:
“How can we make bitcoin tech education more engaging and fun?”
Since then it’s become a game with 10 fun chapters, and support for both Python and JavaScript
Worldwide there are groups like TabConf and Scalar School playing together.
 Give Saving Satoshi a go today, and let us know what you think.
Shoutout to the team that helped bring this over the finish line
Give Saving Satoshi a go today, and let us know what you think.
Shoutout to the team that helped bring this over the finish line
 Now be quick, Satoshi needs you!
www.savingsatoshi.com
Now be quick, Satoshi needs you!
www.savingsatoshi.com Being able to play with interactive elements to understand Bitcoin concepts is the best way to solidify a working mental model
Being able to play with interactive elements to understand Bitcoin concepts is the best way to solidify a working mental model
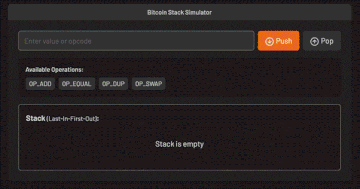 No libraries allowed, you’ll craft everything from scratch!
We support both JavaScript and Python (of course!)
Each bitcoin concept comes with its own exercise, so you’ll learn not just how things work, but also when and where to use them.
No libraries allowed, you’ll craft everything from scratch!
We support both JavaScript and Python (of course!)
Each bitcoin concept comes with its own exercise, so you’ll learn not just how things work, but also when and where to use them.
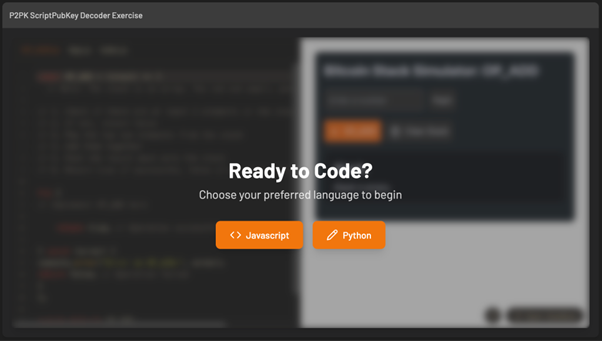 By the end of each module, you’ll challenge yourself by creating a project to test your understanding.
By the end of each module, you’ll challenge yourself by creating a project to test your understanding.
 We’ve started with the first module on Scripts.
More content is coming soon!
Please share your feedback on this first release—it helps us understand what you want to see next, whether it’s content or new features.
We’ve started with the first module on Scripts.
More content is coming soon!
Please share your feedback on this first release—it helps us understand what you want to see next, whether it’s content or new features.
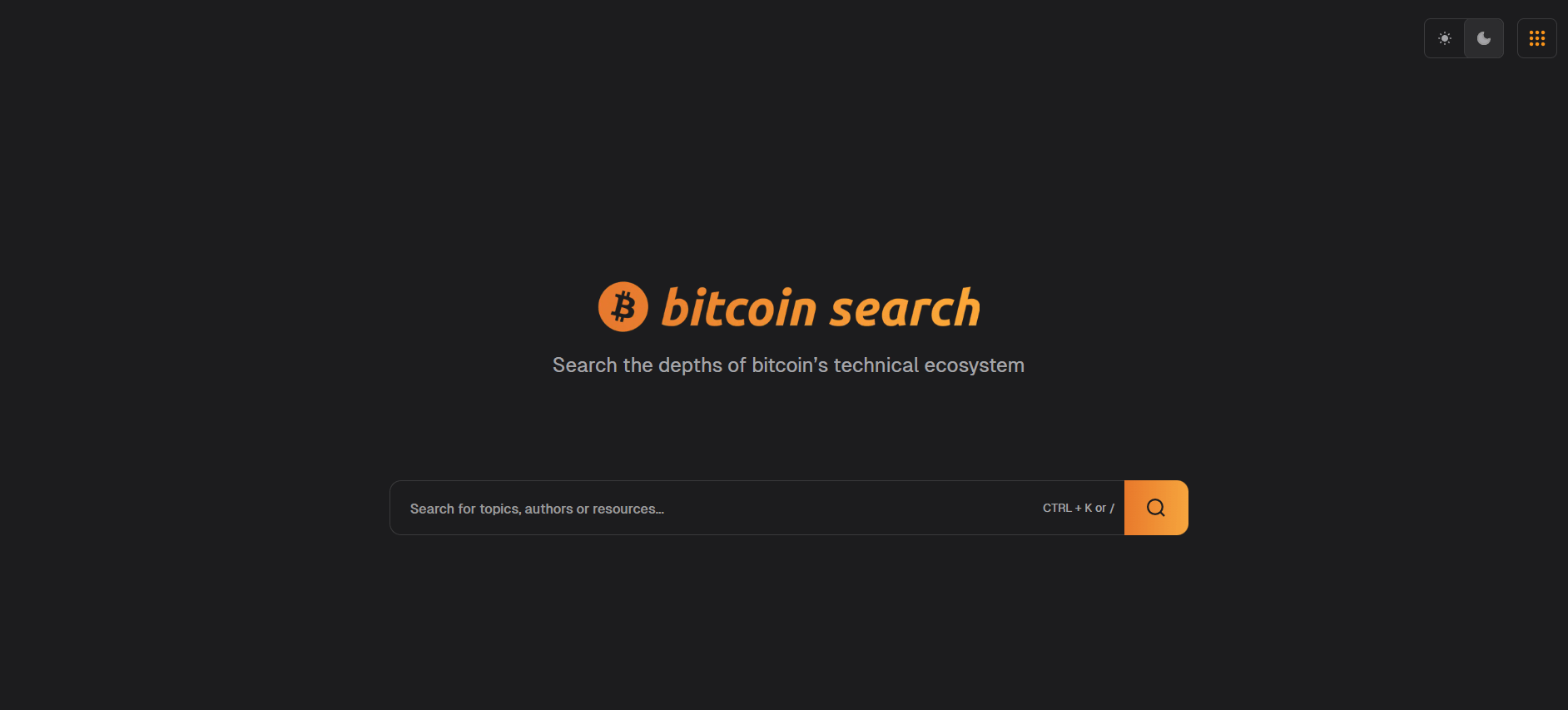
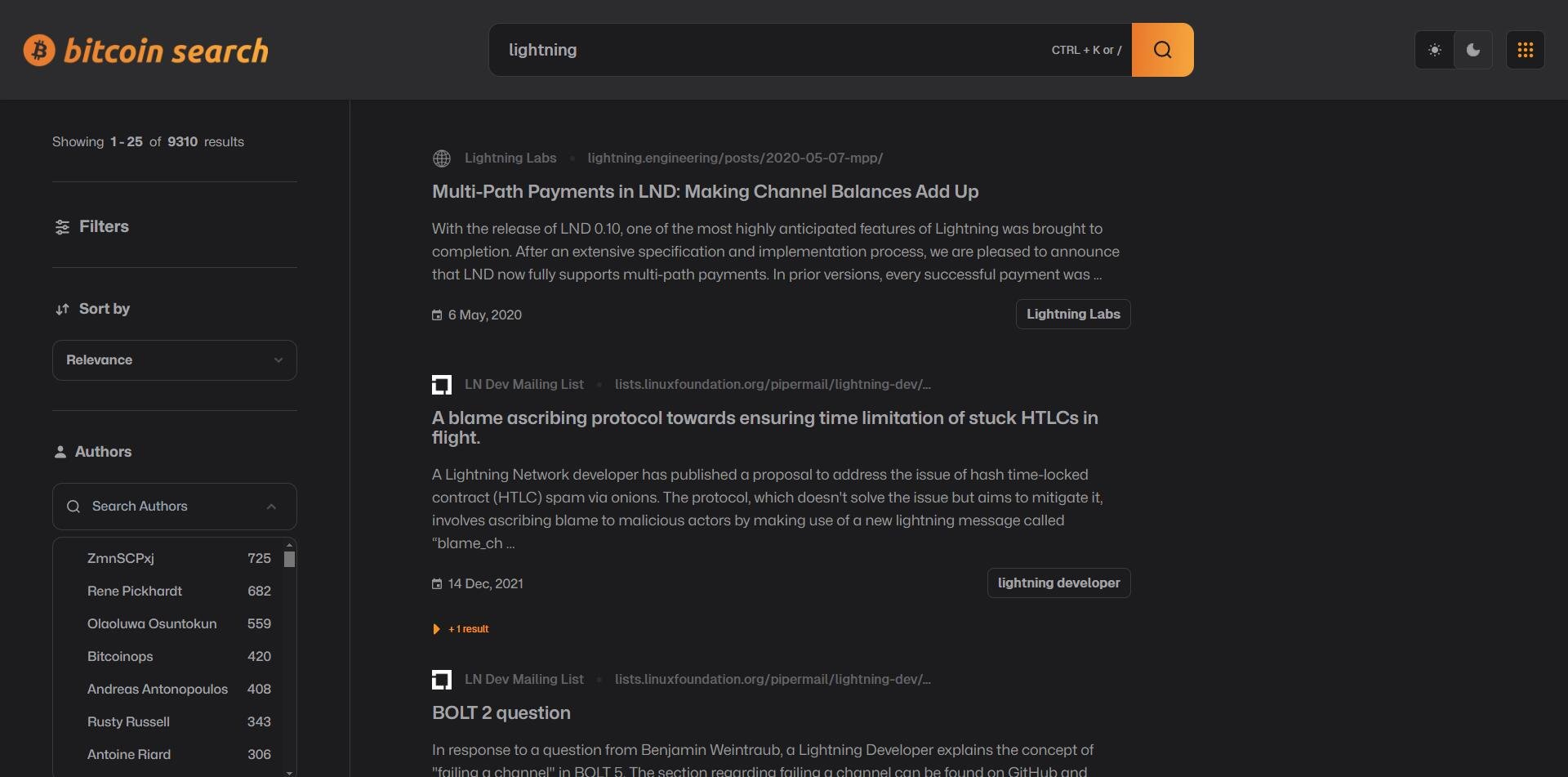 Features
We let you sort and filter by categories that matter
- Authors and
- Sources
And in ways that matter
- Relevance and
- Date
And with views you love: dark 🌑 & light 🌞
Scope
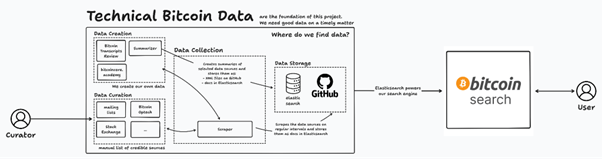
The scope of the product is laser focused: bitcoin tech
Users can suggest sources deeper in the product. This bolsters our repo of bitcoin tech sources
We build pathways to scrape the data
Which grows our library of bitcoin tech literature and resources
Ecosystem of Knowledge Creation
Bitcoin Search thrives as a collaborative ecosystem.
As you do more Transcript Reviews and suggest new credible sources, our database continuously expands and improves, ultimately benefiting the entire Bitcoin technical community.
It’s a virtuous cycle of knowledge creation
Features
We let you sort and filter by categories that matter
- Authors and
- Sources
And in ways that matter
- Relevance and
- Date
And with views you love: dark 🌑 & light 🌞
Scope
The scope of the product is laser focused: bitcoin tech
Users can suggest sources deeper in the product. This bolsters our repo of bitcoin tech sources
We build pathways to scrape the data
Which grows our library of bitcoin tech literature and resources
Ecosystem of Knowledge Creation
Bitcoin Search thrives as a collaborative ecosystem.
As you do more Transcript Reviews and suggest new credible sources, our database continuously expands and improves, ultimately benefiting the entire Bitcoin technical community.
It’s a virtuous cycle of knowledge creation
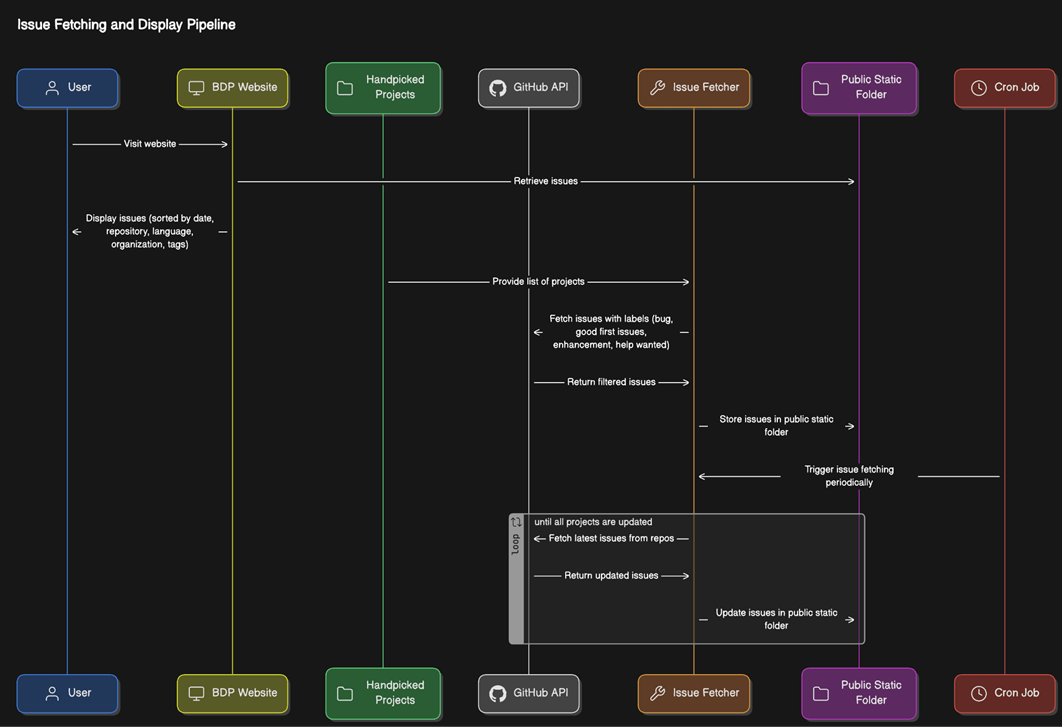
 We already had a live V1. Why build a V2?
We wanted to improve comprehension of the product for newer devs interested in bitcoin tech
While improving its usability, and increasing a sense of delight when using it.
We already had a live V1. Why build a V2?
We wanted to improve comprehension of the product for newer devs interested in bitcoin tech
While improving its usability, and increasing a sense of delight when using it.
 Biggest thanks to the team!
Dev: Emmanuel, Solomon, Balogun, Otuedon
Design:
Biggest thanks to the team!
Dev: Emmanuel, Solomon, Balogun, Otuedon
Design: 
 🖤 Biggest thanks to our team!
- Vision: Theo
- Ideation: Emmanuel, Solomon, Abubakar Ismail
- Design: Theo with thanks to paperpsych
- Dev: Theo, Solomon, Balogun
- Product:
🖤 Biggest thanks to our team!
- Vision: Theo
- Ideation: Emmanuel, Solomon, Abubakar Ismail
- Design: Theo with thanks to paperpsych
- Dev: Theo, Solomon, Balogun
- Product: