We are very grateful to those who repost our notes; it is the most crucial way for our ideas to reach more people.
We write explanatory notes to help more people understand what makes a good chat app and can verify Keychat's design for themselves. View quoted note →

Keychat
npub1h0uj...rwx8
Keychat is the super app for Bitcoiners.
Sovereign IDs, Bitcoin Wallet, Secure Chat, Mini Apps — all in Keychat.
Sovereign. Security. Richness
Contact us for feedback 👇
https://www.keychat.io/u/?k=npub1h0uj825jgcr9lzxyp37ehasuenq070707pj63je07n8mkcsg3u0qnsrwx8
Designing a DM for a microblogging app is not the same as designing a chat app.
A chat app opts for better security while accepting poorer multi-device synchronization capabilities.
A DM opts for better multi-device synchronization capabilities while accepting weaker security.
We need to determine what our primary goal is, make trade-offs, and recognize that there is no perfect solution.
As reflected in the note below, the advantages and disadvantages of NIP-17 are two sides of the same coin. View quoted note →
Many people want it. View quoted note →
Old Nostr DM (NIP-4) integrates four capabilities into a single Nostr key—it serves as an ID, an encryption key, a receiving address, and a sending address.
The encryption key in NIP-4 does not change, so NIP-4 messages lack both forward secrecy and backward secrecy.
Consequently, if the private key is compromised, both historical and future messages can be exposed.
The receiving and sending addresses remain constant, which poses a severe issue for metadata privacy in NIP-4 messages;
Everyone can see who (ID) is sending messages to whom (ID).
Currently, most Nostr apps use NIP-4 for DM functionalities, such as Damus and Primal.
——————————————————————————————————————
New Nostr DM (NIP-17) integrates three capabilities into a single Nostr key—it serves as an ID, an encryption key, and a receiving address.
Kind-17 separates the sending address from the ID, making the sending address random and concealing the sender's real ID, thus improving metadata privacy.
The encryption key in NIP-17 does not change, so NIP-17 messages also lack forward secrecy and backward secrecy. Once the private key is leaked, both historical and future messages will be compromised.
The receiving address remains constant, so there is still a slight issue with metadata privacy in NIP-17 messages; everyone can see who (ID) is receiving messages.
Apps like 0xchat and Amethyst use NIP-17 to implement DM functionalities.
——————————————————————————————————————
In Keychat, the ID, encryption key, receiving address, and sending address are separated.
The encryption key, the receiving address, and the sending address are updated independently and continuously.
Keychat's encryption key is derived using the Signal protocol, and each message uses a unique encryption key, which is deleted after use.
Thus, Keychat messages have both forward secrecy and backward secrecy. Even if an encryption key is compromised, only the current message can be leaked, and historical and future messages remain secure.
Keychat's sending address is randomly generated for each message.
Therefore, external parties do not know the sender's ID.
Keychat's receiving address is derived using the Signal protocol, with almost every message using a unique receiving address.
Thus, external parties do not know the receiver's ID.
——————————————————————————————————————
However, it's important to emphasize that NIP-4 and NIP-17 offer superior multi-device synchronization capabilities because they integrate three capabilities into a single Nostr key—it serves as an ID, an encryption key, and a receiving address.
“The Signal protocol is used by two parties to exchange encrypted messages based on a shared secret key.”
“Messaging Layer Security (MLS) is a security layer for encrypting messages in groups ranging from two to many.”
So, it might seem logical to conclude that "the MLS protocol is a superset of the Signal protocol, and the Signal protocol is a subset of the MLS protocol. Whether it's one-on-one private chats, small group chats, or large group chats, the MLS protocol alone could be used to implement them."
However, this seemingly logical conclusion is incorrect.
The MLS protocol is not as efficient as the Signal protocol for implementing one-on-one chats and small group chats.
Assume a two-person MLS group chat and a one-on-one chat using the Signal protocol, both achieving the same level of security.
In the MLS group, each message sent requires an additional message to update the encryption key (with forward secrecy and backward secrecy capabilities).
In contrast, one-on-one chats using the Signal protocol do not require this additional message to update the encryption key (with forward secrecy and backward secrecy capabilities). View quoted note →
The Signal protocol, primarily known for its double ratchet algorithm, is used for end-to-end encryption of messages by the following chat applications and protocols. Many users are unaware that they are already benefiting from the security offered by the Signal protocol.
Chat Applications:
Signal app
WhatsApp
Skype: only available in the "Private Conversation"
Facebook Messenger: only available in the "Secret Conversations”
Simplex chat
Keychat
Chat Protocols:
XMPP
OMEMO is an XMPP Extension Protocol (XEP) for secure multi-client end-to-end encryption. It is an open standard based on a Double Ratchet and PEP, which can be freely used and implemented by anyone.
 Matrix
Olm (libolm) is an independent Apache-licensed implementation of the Double Ratchet cryptographic ratchet in C & C++, which also includes the new Megolm group ratchet as used in Matrix.
Matrix
Olm (libolm) is an independent Apache-licensed implementation of the Double Ratchet cryptographic ratchet in C & C++, which also includes the new Megolm group ratchet as used in Matrix.
 View quoted note →
View quoted note →

OMEMO Multi-End Message and Object Encryption
An XMPP Extension Protocol based on a Double Ratchet and PEP which can be freely used and implemented by anyone. The protocol has been audited by ...
GitHub
GitHub - matrix-org/olm: An implementation of the Double Ratchet cryptographic ratchet in C++/C
An implementation of the Double Ratchet cryptographic ratchet in C++/C - matrix-org/olm
Have you ever been curious about how the group chats are actually implemented?
Or have you assumed that group chats are as secure as one-on-one chats? View quoted note →
1/n
Group chats with end-to-end encryption can be designed in many ways, each tailored for a specific number of participants and level of security.
If we regard the security of one-on-one chats in Keychat as perfect, scoring 100, and the security of large group chats without end-to-end encryption as nonexistent, scoring 0, we can map out where the five identified end-to-end encryption group chat models fall in terms of group size and security on a diagram as shown below: 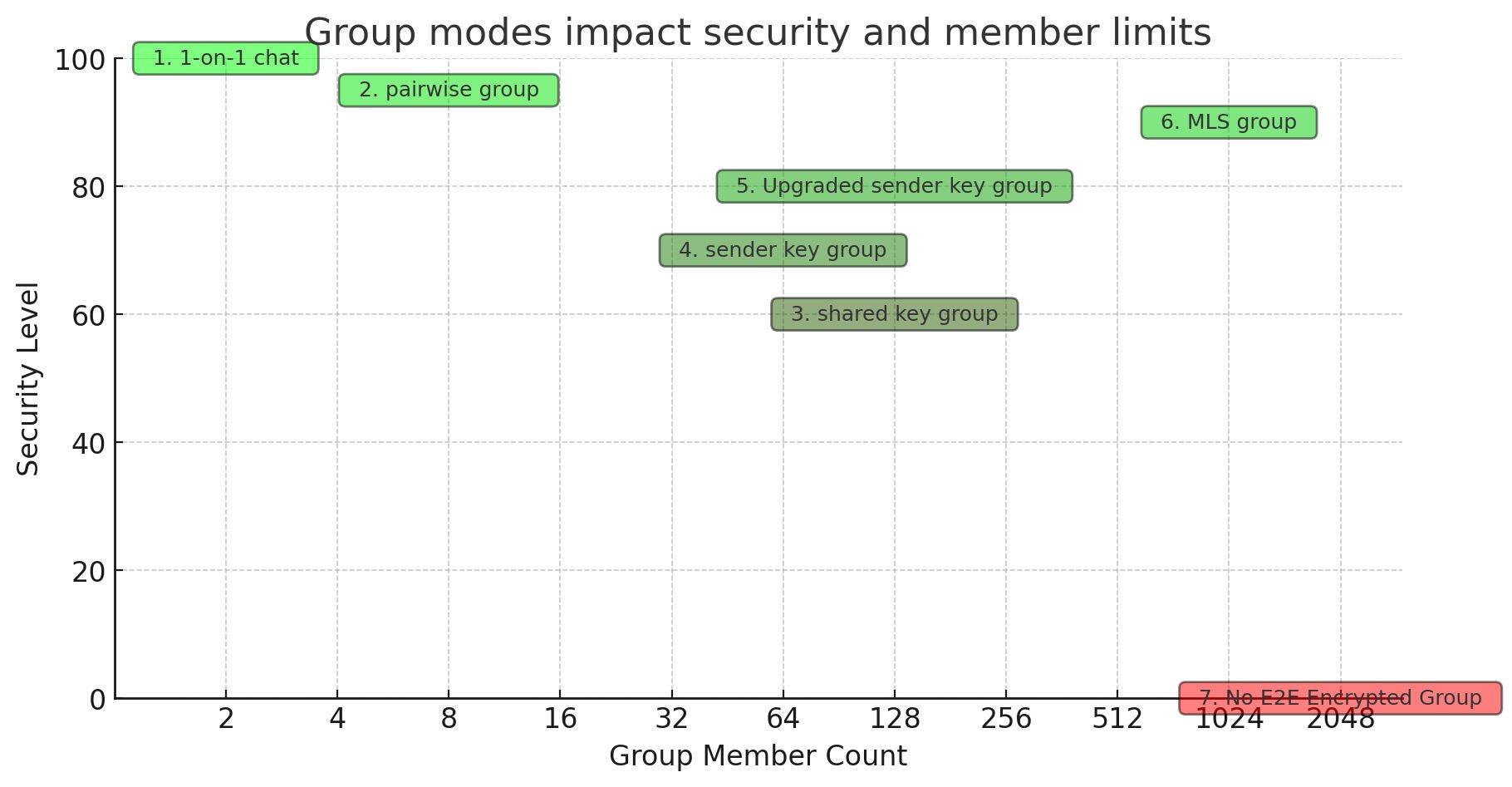

The Signal protocol and the MLS (Message Layer Security) protocol are both designed for end-to-end encryption of messages.
The Signal protocol is particularly suited for one-on-one chats and small group. On the other hand, the MLS protocol is more appropriate for larger group.
Both can be implemented on Nostr.
If you are interested in understanding the basic principles of these protocols, I highly recommend the following two videos:
@calle Calle's speech starts at 55:40, a fantastic presentation.
https://www.youtube.com/live/Zv766SV840k 


We hope more people can have their own Lightning Network channels, enabling them to have self-custodial LN wallets.
If new users (who doesn't yet have their own LN channel) needs to receive LN sats, but the amount is not sufficient to open a LN channel (due to the need to pay an on-chain transaction fee), they can use the LN channel of a trusted ecash mint to receive them.
The ecash mint gives them ecash sats. Once they have accumulated enough ecash sats, they can open their own LN channel.
Ecash sat is a bridge to self-custodial LN sat. 
 View quoted note →
View quoted note →


One of the pursuits of a good chat application is to simulate face-to-face conversation in cyberspace, just like in a physical space, where sound waves travel from one person's mouth to another's ear and then dissipate forever. Only these two people know the content of the conversation. View quoted note →
We are very pleased that more and more people recognize the model of using ecash sat as message stamps.
We believe that this seemingly trivial 1 sat is like a butterfly flapping its wings, capable of producing an unexpected butterfly effect. View quoted note →
Simplex Chat is very popular in the Nostr community; whenever someone posts a note asking which chat app is secure, many people recommend Simplex Chat. We also think Simplex Chat is a great app.
So, many people ask what is the difference between Keychat and Simplex Chat? Is Keychat's security as good as Simplex Chat's? Is it really possible to create a chat app as secure as Simplex Chat on Nostr? Why not just use Simplex Chat? Why reinvent the wheel?
A common misconception in the Nostr community is that Nostr is not suitable for private things.
"Nothing about any of the protocols we’ve developed requires centralization; it’s entirely possible to build a federated Signal Protocol-based messenger, but I no longer believe that it is possible to build a competitive federated messenger at all." — Signal Founder Moxie https://signal.org/blog/the-ecosystem-is-moving%C2%A0
This is because the encryption process is completed on the client side, and relays only pass the encrypted messages.
Keychat and Simplex Chat both use the Signal protocol to encrypt messages, so both meet the following security requirements 1-4:
Anti-Forgery
Anti-Forgery ensures that the sender of a message is verifiable and the message has not been tampered with.
End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption ensures that only the sender and receiver can decrypt and read the message content, protecting it from unauthorized access by servers or other network devices.
Forward Secrecy
Forward secrecy ensures that even if the current key is compromised, historical messages cannot be decrypted, since each message uses a new encryption key, which is deleted after use.
Break-in Recovery
Break-in Recovery ensures that if the current key is compromised, future messages cannot be decrypted, and the system can recover from the attack. This feature is also known as backward secrecy.
Metadata Privacy
Protecting the privacy of communication involves more than just protecting the content of messages; it also includes protecting the identities of the communication parties and other data.
Regarding the fifth point, metadata privacy. The designs of Keychat and Simplex Chat are different.
Simplex’s metadata privacy protection scheme
"Simplex chat is the first messenger without user IDs."
“To deliver messages, instead of user IDs used by all other platforms, SimpleX uses temporary anonymous pairwise identifiers of message queues, separate for each of your connections — there are no long term identifiers.”
“Temporary anonymous pairwise identifiers
SimpleX uses temporary anonymous pairwise addresses and credentials for each user contact or group member.
It allows to deliver messages without user profile identifiers, providing better meta-data privacy than alternatives.”
We can understand this mechanism as, if a Simplex Chat user has 10 friends, they have 10 IDs, using different IDs with different friends?
Keychat’s metadata privacy protection scheme
Current chat applications and email have forgotten that an address is not the same as an ID, treating the ID as the address. Emails and current chat applications send messages as [from: Alice's ID to: Bob's ID]. Regardless of how your geographical address changes, when Alice sends an email to Bob, it’s always [from: Alice's ID to: Bob's ID]. This compromises metadata privacy.
However, letters work differently; they are [from: Alice's current geographical address to: Bob's current geographical address].
Keychat separates the receiving address and sending addresses from the ID, and the receiving address and sending addresses are also different. Keychat messages are [from: Alice's one-time sending address to: Bob's almost one-time receiving address]. This makes it difficult for outsiders and relay administrators to determine who is sending messages to whom.
Which scheme do you think is easier to understand and better protects metadata privacy?
Finally, Keychat also uses ecash sat as a stamp for messages, with relays funded by stamp revenue to sustain operations.